13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(10):4767-4778. doi:10.7150/thno.70869 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Internally inlaid SaCas9 base editors enable window specific base editing
Laboratory of Biotherapy, National Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, Cancer Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan university, Renmin Nanlu 17, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
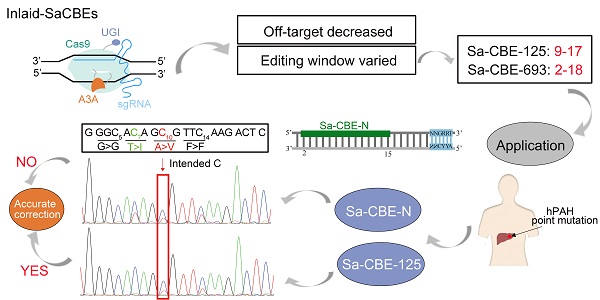
Rationale: Base editors composed of catalytic defective Cas9 and cytosine or adenosine deaminase are powerful tools to convert bases in a genome. However, the fixed and narrow editing window of current base editors has impeded their utility. To increase the scope and diversify the editing patterns is quite necessary.
Methods and Results: We designed a subset of base editors derived from SaCas9 in which deaminase was inlaid into various locations of the SaCas9 protein. The resulting base editors were characterized with multiple genomic sites and were found to have distinct editing features to the N-terminal SaCas9 CBE (Sa-CBE-N). Among them, Sa-CBE-693, in which a cytosine deaminase was inserted between amino acids 693 and 694, showed an increased editing efficiency and a significantly expanded editing window ranging from bases 2-18. This feature enhanced the editing efficiency of BCL11A enhancer that contains multiple consensus bases in a 15-bp fragment. Another variant, Sa-CBE-125, displayed backward-shifted editing window, which we showed was particularly powerful in editing cytosines that were accompanied with unintended bystander cytosines at their 5' side. Additionally, these editors showed reduced Cas9 independent DNA off-target editing compared with Sa-CBE-N.
Conclusion: Our inlaid base editors improved the targeting scope and diversified the editing pattern.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9, base editing, editing window, off-target, thalassemia
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact