13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5645-5674. doi:10.7150/thno.63177 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Therapeutic aptamer targeting sclerostin loop3 for promoting bone formation without increasing cardiovascular risk in osteogenesis imperfecta mice
1. Law Sau Fai Institute for Advancing Translational Medicine in Bone and Joint Diseases (TMBJ), School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong SAR, China
2. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area International Research Platform for Aptamer-based Translational Medicine and Drug Discovery (HKAP), Hong Kong SAR, China
3. Institute of Precision Medicine and Innovative Drug Discovery (PMID), School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong SAR, China
4. Institute of Integrated Bioinformedicine and Translational Science (IBTS), School of Chinese Medicine, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong SAR, China
5. Northwestern Polytechnical University-Hong Kong Baptist University United Research Center of Space Musculoskeletal Health, Shenzhen, China
6. School of Chinese Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, China
7. Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China
8. The Key Laboratory of Aerospace Medicine, Ministry of Education, Air Force Medical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi, China
9. Department of Endocrinology, National Health Commission Key Laboratory of Endocrinology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
10. Shanghai Clinical Research Center of Bone Disease, Department of Osteoporosis and Bone Disease, Shanghai Jiao Tong University Affiliated Sixth People's Hospital, Shanghai, China
11. Department of Wound Repair and Rehabilitation Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Trauma, Burns and Combined Injury, Trauma Center, Research Institute of Surgery, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China
12. Orthopedic Center, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University (People's Hospital of Shenzhen Baoan District), Shenzhen, China
# Luyao Wang, Yuanyuan Yu, Shuaijian Ni, and Dijie Li contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
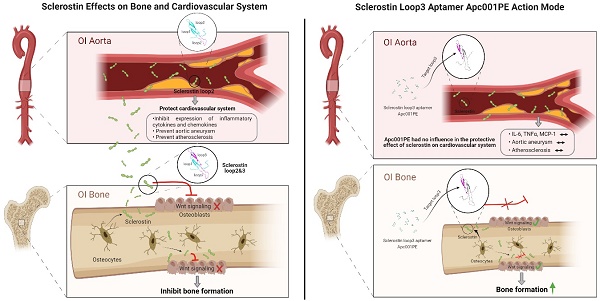
Rationale: Sclerostin inhibition demonstrated bone anabolic potential in osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) mice, whereas humanized therapeutic sclerostin antibody romosozumab for postmenopausal osteoporosis imposed clinically severe cardiac ischemic events. Therefore, it is desirable to develop the next generation sclerostin inhibitors to promote bone formation without increasing cardiovascular risk for OI.
Methods and Results: Our data showed that sclerostin suppressed inflammatory responses, prevented aortic aneurysm (AA) and atherosclerosis progression in hSOSTki.Col1a2+/G610C.ApoE-/- mice. Either loop2&3 deficiency or inhibition attenuated sclerostin's suppressive effects on expression of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in vitro, whilst loop3 deficiency maintained the protective effect of sclerostin on cardiovascular system both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, loop3 was critical for sclerostin's antagonistic effect on bone formation in Col1a2+/G610C mice. Accordingly, a sclerostin loop3-specific aptamer aptscl56 was identified by our lab. It could recognize both recombinant sclerostin and sclerostin in the serum of OI patients via targeting loop3. PEG40k conjugated aptscl56 (Apc001PE) demonstrated to promote bone formation, increase bone mass and improve bone microarchitecture integrity in Col1a2+/G610C mice via targeting loop3, while did not show influence in inflammatory response, AA and atherosclerosis progression in Col1a2+/G610C.ApoE-/- mice with Angiotensin II infusion. Further, Apc001PE had no influence in the protective effect of sclerostin on cardiovascular system in hSOSTki.Col1a2+/G610C.ApoE-/- mice, while it inhibited the antagonistic effect of sclerostin on bone formation in hSOSTki.Col1a2+/G610C mice via targeting loop3. Apc001PE was non-toxic to healthy rodents, even at ultrahigh dose. Apc001PE for OI was granted orphan drug designation by US-FDA in 2019 (DRU-2019-6966).
Conclusion: Sclerostin loop3-specific aptamer Apc001PE promoted bone formation without increasing cardiovascular risk in OI mice.
Keywords: Aptamer, sclerostin loop3, osteogenesis imperfecta, bone formation, no cardiovascular risk, no toxicity
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact