13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5710-5726. doi:10.7150/thno.71832 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Continuous theta-burst stimulation enhances and sustains neurogenesis following ischemic stroke
1. Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, 211166, China
2. Emergency Center, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, 221002, China
3. Department of Neurology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, 221002, China
4. Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, 221004, China
5. Augusta University, Augusta, Georgia, 30912, USA
Abstract
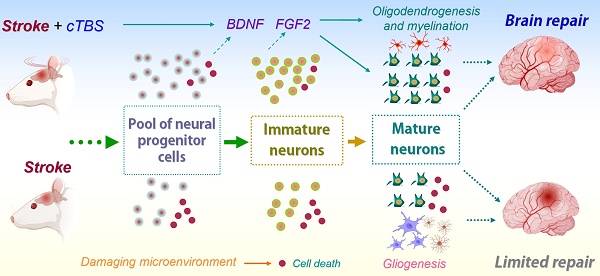
Rationale: Previous work has indicated that continuous theta-burst stimulation (cTBS), a modality of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), may provide neuroprotection and improve neurological function after stroke by preserving the blood-brain barrier, altering glial polarization phenotypes, and supporting peri-infarct angiogenesis. The present study was performed to examine whether cTBS, a noninvasive neurostimulation technique, promotes neurogenesis in a photothrombotic (PT) stroke rat model and contributes to functional recovery.
Methods: Beginning 3 h or 1 week after the induction of PT stroke, once-daily 5-min cTBS treatments were applied to the infarcted hemisphere for 6 days. Samples were collected 6 days, 22 days, and 35 days after PT stroke. Fluorescent labeling, Western blotting, and behavioral tests were performed accordingly.
Results: We found that cTBS therapy significantly expanded the pool of neural progenitor cells (NPCs) and newly generated immature neurons in the cortical peri-infarct region after PT stroke. Likewise, the amount of DCX-positive immature neurons in the peri-infarct area was markedly elevated by cTBS. Application of cTBS strikingly diminished the PT-induced loss of NPCs and newly-formed neurons. In addition, the amount of newly generated mature neurons in the peri-infarct zone was significantly promoted by cTBS. Intriguingly, cTBS reduced reactive gliogenesis significantly while promoting oligodendrogenesis and preserving myelination. Mechanistic studies uncovered that cTBS upregulated brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2). Finally, cTBS-treated animals displayed improved motor functions. To be noted, temozolomide (TMZ), a drug that has been previously used to suppress neurogenesis, could reverse the beneficial effects of cTBS.
Conclusions: Our findings provide new insight into the mechanism by which cTBS promotes functional recovery from stroke. We demonstrated that cTBS effectively enhances and sustains neurogenesis after PT stroke. Both early and delayed cTBS treatment could improve the survival of newly generated neurons and functional recovery, and inhibition of neurogenesis could reverse these therapeutic benefits. Mechanistically, cTBS was effective in upregulating the release of neurotrophic factors, protecting NPC and immature neurons, as well as suppressing excessive gliogenesis.
Keywords: Ischemic stroke, Continuous theta-burst stimulation (cTBS), Neurogenesis, Functional recovery, Neurotrophic factors
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact