13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(13):5971-5985. doi:10.7150/thno.75336 This issue Cite
Research Paper
3p-C-NETA: A versatile and effective chelator for development of Al18F-labeled and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals
1. NURA, Belgian Nuclear Research Center (SCK CEN), Mol, Belgium.
2. Radiopharmaceutical Research, Department of Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological sciences, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
3. Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
4. Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Department of Imaging and Pathology, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
5. Department of Medical Imaging, College of Medicine, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada.
6. Department of Chemistry, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
7. Life Sciences Division, TRIUMF, Vancouver, Canada.
8. Department of Medical Imaging, Royal University Hospital (RUH), Saskatoon, Canada.
9. Biomedical MRI/MoSAIC, Department of Imaging and Pathology, Biomedical Sciences Group, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium.
Abstract
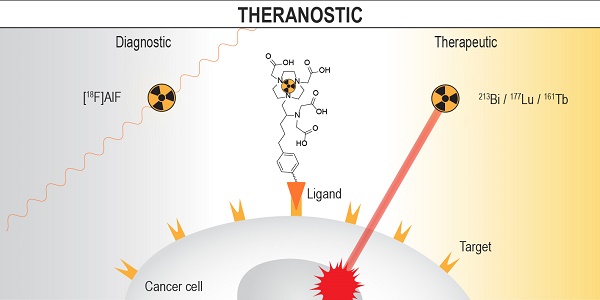
Background: Radiolabeled somatostatin analogues (e.g. [68Ga]Ga-DOTATATE and [177Lu]Lu-DOTATATE) have been used to diagnose, monitor, and treat neuroendocrine tumour (NET) patients with great success. [18F]AlF-NOTA-octreotide, a promising 18F-labeled somatostatin analogue and potential alternative for 68Ga-DOTA-peptides, is under clinical evaluation. However, ideally, the same precursor (combination of chelator-linker-vector) can be used for production of both diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals with very similar (e.g. Al18F-method in combination with therapeutic radiometals 213Bi/177Lu) or identical (e.g. complementary Tb-radionuclides) pharmacokinetic properties, allowing for accurate personalised dosimetry estimation and radionuclide therapy of NET patients. In this study we evaluated 3p-C-NETA, as potential theranostic Al18F-chelator and present first results of radiosynthesis and preclinical evaluation of [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE.
Methods: 3p-C-NETA was synthesized and radiolabeled with diagnostic (68Ga, Al18F) or therapeutic (177Lu, 161Tb, 213Bi, 225Ac and 67Cu) radionuclides at different temperatures (25-95 °C). The in vitro stability of the corresponding radiocomplexes was determined in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and human serum. 3p-C-NETA-TATE was synthesized using standard solid/liquid-phase peptide synthesis. [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE was synthesized in an automated AllinOne® synthesis module and the in vitro stability of [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE was evaluated in formulation buffer, PBS and human serum. [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE pharmacokinetics were evaluated using µPET/MRI in healthy rats, with [18F]AlF-NOTA-Octreotide as benchmark.
Results: 3p-C-NETA quantitatively sequestered 177Lu, 213Bi and 67Cu at 25 °C while heating was required to bind Al18F, 68Ga, 161Tb and 225Ac efficiently. The [18F]AlF-, [177Lu]Lu- and [161Tb]Tb-3p-C-NETA-complex showed excellent in vitro stability in both PBS and human serum over the study period. In contrast, [67Cu]Cu- and [225Ac]Ac-, [68Ga]Ga-3p-C-NETA were stable in PBS, but not in human serum. [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE was obtained in good radiochemical yield and radiochemical purity. [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE displayed good in vitro stability for 4 h in all tested conditions. Finally, [18F]AlF-3p-C-NETA-TATE showed excellent pharmacokinetic properties comparable with the results obtained for [18F]AlF-NOTA-Octreotide.
Conclusions: 3p-C-NETA is a versatile chelator that can be used for both diagnostic applications (Al18F) and targeted radionuclide therapy (213Bi, 177Lu, 161Tb). It has the potential to be the new theranostic chelator of choice for clinical applications in nuclear medicine.
Keywords: 3p-C-NETA, Al18F, PET, targeted radionuclide therapy, radiopharmaceutical
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact