13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(14):6106-6129. doi:10.7150/thno.72800 This issue Cite
Review
Immunotherapy in soft tissue and bone sarcoma: unraveling the barriers to effectiveness
1. Cancer Biophysics Laboratory, Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus.
2. Medical School, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus.
3. Bank of Cyprus Oncology Centre, Nicosia, Cyprus.
4. Cyprus Cancer Research Institute, Nicosia, Cyprus.
Abstract
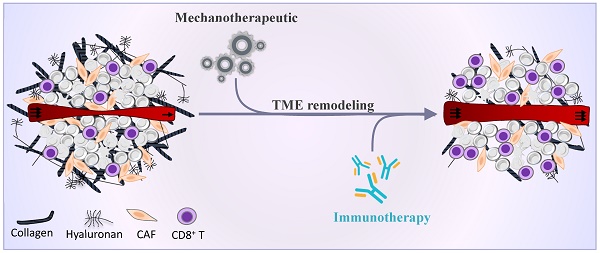
Sarcomas are uncommon malignancies of mesenchymal origin that can arise throughout the human lifespan, at any part of the body. Surgery remains the optimal treatment modality whilst response to conventional treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation, is minimal. Immunotherapy has emerged as a novel approach to treat different cancer types but efficacy in soft tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma is limited to distinct subtypes. Growing evidence shows that cancer-stroma cell interactions and their microenvironment play a key role in the effectiveness of immunotherapy. However, the pathophysiological and immunological properties of the sarcoma tumor microenvironment in relation to immunotherapy advances, has not been broadly reviewed. Here, we provide an up-to-date overview of the different immunotherapy modalities as potential treatments for sarcoma, identify barriers posed by the sarcoma microenvironment to immunotherapy, highlight their relevance for impeding effectiveness, and suggest mechanisms to overcome these barriers.
Keywords: tumor microenvironment, immunosuppression, hypoxia, tumor normalization, mechanotherapeutics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact