13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2022; 12(14):6380-6394. doi:10.7150/thno.74828 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Cerenkov luminescence imaging of interscapular brown adipose tissue using a TSPO-targeting PET probe in the UCP1 ThermoMouse
1. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2. Department of Biomedical Sciences, Seoul National University Graduate School, Seoul, Republic of Korea
3. Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
4. Cancer Imaging Center, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea
5. Radiation Medicine Research Institute, Medical Research Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
6. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Republic of Korea
7. Center for Nanomolecular Imaging and Innovative Drug Development, Advanced Institutes of Convergence Technology, Seoul National University, Suwon, Republic of Korea
# These authors equally contributed to this research.
Abstract
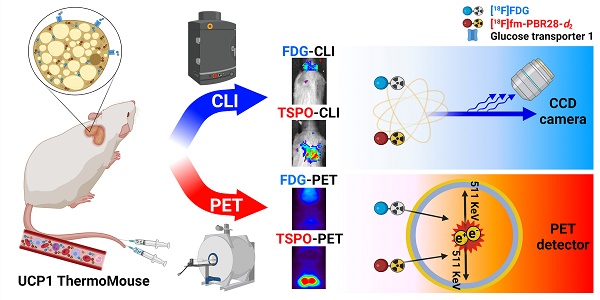
Rationale: [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography ([18F]FDG-PET) has been widely used as an imaging technique to measure interscapular brown adipose tissue (iBAT) activity. However, it is challenging to obtain iBAT-specific images using [18F]FDG-PET because increased uptake of [18F]FDG is observed in tumors, muscle, and inflamed tissues. Uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1) in the mitochondrial membrane, a well-known molecular marker of BAT, has been proposed as a useful BAT imaging marker. Recently, the UCP1 ThermoMouse was developed as a reporter mouse for monitoring UCP1 expression and investigating BAT activation. In addition, Translocator protein-18 kDa (TSPO) located in the outer mitochondrial membrane is also overexpressed in BAT, suggesting that TSPO-targeting PET has potential for iBAT imaging. However, there are no studies monitoring BAT using TSPO-targeting PET probes in the UCP1 ThermoMouse. Moreover, the non-invasive Cerenkov luminescence imaging (CLI) using Cerenkov radiation from the PET probe has been proposed as an alternative option for PET as it is less expensive and user-friendly. Therefore, we selected [18F]fm-PBR28-d2 as a TSPO-targeting PET probe for iBAT imaging to evaluate the usefulness of CLI in the UCP1 ThermoMouse.
Methods: UCP1 ThermoMouse was used to monitor UCP1 expression. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry were performed to measure the level of protein expression. [18F]fm-PBR28-d2 and [18F]FDG were used as radioactive probes for iBAT imaging. PET images were acquired with SimPET, and optical images were acquired with IVIS 100.
Results: UCP1 ThermoMouse showed that UCP1 and TSPO expressions were correlated in iBAT. In both PET and CLI, the TSPO-targeting probe [18F]fm-PBR28-d2 was superior to [18F]FDG for acquiring iBAT images. The high molar activity of the probe was essential for CLI and PET imaging. We tested the feasibility of TSPO-targeting probe under cold exposure by imaging with TSPO-PET/CLI. Both signals of iBAT were clearly increased after cold stimulation. Under prolonged isoflurane anesthesia, TSPO-targeting images showed higher signals from iBAT in the short-term than in long-term groups.
Conclusion: We demonstrated that TSPO-PET/CLI reflected UCP1 expression in iBAT imaging better than [18F]FDG-PET/CLI under the various conditions. Considering convenience and cost, TSPO-CLI could be used as an alternative TSPO-PET technique for iBAT imaging.
Keywords: Interscapular brown adipose tissue, UCP1, TSPO, PET, Cerenkov luminescence imaging
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact