13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(1):355-373. doi:10.7150/thno.77560 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Size-advantage of monovalent nanobodies against the macrophage mannose receptor for deep tumor penetration and tumor-associated macrophage targeting
1. Unit of Advanced Optical Microscopy, IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital -, via Manzoni 56, 20089 Rozzano, Milan, Italy.
2. Department of Biomedical Sciences, Humanitas University, Via Rita Levi Montalcini 4, 20090 Pieve Emanuele, Milan, Italy.
3. IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital -, via Manzoni 56, 20089 Rozzano, Milan, Italy.
4. Cellular and Molecular Immunology Lab, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium (Pleinlaan 2, 1050 Brussels).
5. Myeloid Cell Immunology Lab, VIB Center for Inflammation Research, Brussels, Belgium.
6. Laboratory for In vivo Cellular and Molecular Imaging (ICMI-BEFY/MIMA), Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium (Laarbeeklaan 103, 1090 Brussels).
7. Leiden University Medical Center, Interventional Molecular Imaging Laboratory, Albinusdreef 2 2333 ZA Leiden.
8. The William Harvey Research Institute, Queen Mary University of London, London EC1M6BQ, UK.
* Equal contribution
Abstract
Rationale: Nanobodies (Nbs) have emerged as an elegant alternative to the use of conventional monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy, but a detailed microscopic insight into the in vivo pharmacokinetics of different Nb formats in tumor-bearers is lacking. This is especially relevant for the recognition and targeting of pro-tumoral tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), which may be located in less penetrable tumor regions.
Methods: We employed anti-Macrophage Mannose Receptor (MMR) Nbs, in a monovalent (m) or bivalent (biv) format, to assess in vivo TAM targeting. Intravital and confocal microscopy were used to analyse the blood clearance rate and targeting kinetics of anti-MMR Nbs in tumor tissue, healthy muscle tissue and liver. Fluorescence Molecular Tomography was applied to confirm anti-MMR Nb accumulation in the primary tumor and in metastatic lesions.
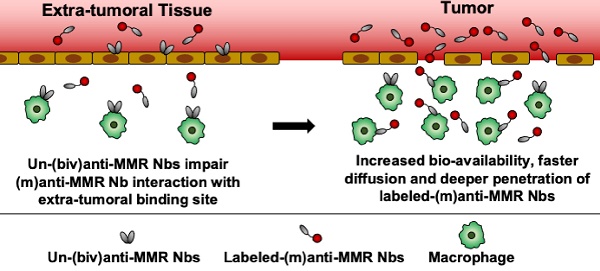
Results: Intravital microscopy demonstrated significant differences in the blood clearance rate and macrophage targeting kinetics of (m) and (biv)anti-MMR Nbs, both in tumoral and extra-tumoral tissue. Importantly, (m)anti-MMR Nbs are superior in reaching tissue macrophages, an advantage that is especially prominent in tumor tissue. The administration of a molar excess of unlabelled (biv)anti-MMR Nbs increased the (m)anti-MMR Nb bioavailability and impacted on its macrophage targeting kinetics, preventing their accumulation in extra-tumoral tissue (especially in the liver) but only partially influencing their interaction with TAMs. Finally, anti-MMR Nb administration not only allowed the visualization of TAMs in primary tumors, but also at a distant metastatic site.
Conclusions: These data describe, for the first time, a microscopic analysis of (m) and (biv)anti-MMR Nb pharmacokinetics in tumor and healthy tissues. The concepts proposed in this study provide important knowledge for the future use of Nbs as diagnostic and therapeutic agents, especially for the targeting of tumor-infiltrating immune cells.
Keywords: tumor-associated macrophage targeting, macrophage mannose receptor, single-domain antibody, intravital microscopy, pharmacokinetics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact