13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(1):403-416. doi:10.7150/thno.76879 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A labeling strategy for the three-dimensional recognition and analysis of microvascular obstruction in ischemic stroke
1. Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics - MoE Key Laboratory for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics - Advanced Biomedical Imaging Facility, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, China.
2. Optics Valley Laboratory, Hubei 430074, China.
Abstract
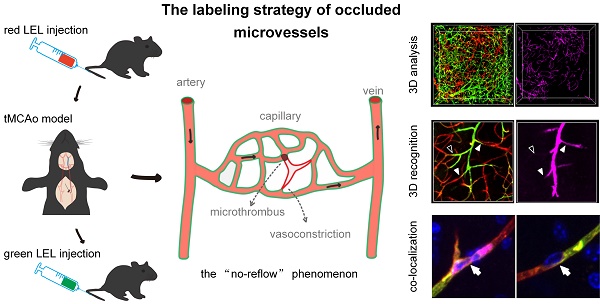
Rationale: Large vessel recanalization in ischemic stroke does not always go along with tissue reperfusion, a phenomenon called “no-reflow”. However, knowledge of the mechanism of no-reflow is limited because identifying microvascular obstruction across the cortex and subcortex both in clinical and experimental models is challenging. In this study, we developed a smart three-dimensional recognition pipeline for microvascular obstruction during post-ischemia reperfusion to examine the underlying mechanism of no-reflow.
Methods: Transient (60 min) occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (tMCAo) in mice was induced using a filament. Two different fluorophore-conjugated tomato lectins were injected into mice via the tail vein before and after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R), respectively, one to label all blood vessels and the other to label functional blood vessels. Post-I/R microvascular obstruction was visualized using combined iDISCO+-based tissue clearing and optical imaging. Arterioles and capillaries were distinguished using whole-mount immunolabeling with an anti-αSMA antibody. Circulating neutrophils were depleted utilizing an anti-Ly6G antibody. Brain slices were immunostained with the anti-Ly6G antibody to identify co-localized blockage points and neutrophils. MATLAB software was used to quantify the capillary diameters in the ipsilateral brain from the normal and tMCAo mice.
Results: Microcirculatory reperfusion deficit worsened over time after I/R. Microvascular obstruction occurred not only in arterioles but also in capillaries, with capillary obstruction associated with local capillary lumen narrowing. In addition, the depletion of circulating neutrophils mitigated reperfusion deficit to a large extent after I/R. The co-localization of blockage points and neutrophils revealed that some neutrophils plugged capillaries with coexisting capillary lumen narrowing and that no neutrophil was trapped in heaps of blockage points. Quantification of the capillary diameter showed that capillary lumen shrunk after I/R but returned to typical measurements when intravascular neutrophils were depleted.
Conclusions: According to our findings, both vascular lumen narrowing and neutrophil trapping in cerebral microcirculation are the key causes of microvascular obstruction after I/R. Also, the primary contribution by neutrophils to microvascular obstruction does not occur through microemboli plugging but rather via the exacerbation of capillary lumen narrowing. Our proposed method will help monitor microcirculatory reperfusion deficit, explore the mechanism of no-reflow, and evaluate the curative effect of drugs targeting no-reflow.
Keywords: microvascular obstruction, three-dimensional recognition, no-reflow, vascular lumen narrowing, neutrophil
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact