13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(12):4197-4216. doi:10.7150/thno.84059 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Preconditioned extracellular vesicles from hypoxic microglia reduce poststroke AQP4 depolarization, disturbed cerebrospinal fluid flow, astrogliosis, and neuroinflammation
1. Department of Neurology, University of Göttingen Medical School, Göttingen, Germany.
2. Department of Neurology, University Hospital Essen, University of Duisburg-Essen, Essen, Germany.
3. Department of Neurology, University of Giessen Medical School, Giessen, Germany.
4. Department of Physiology, Istanbul Medeniyet University, Istanbul, Turkey.
5. Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Medical University of Varna, Varna, Bulgaria.
6. Center for Mind, Brain and Behavior (CMBB), University of Marburg and Justus Liebig University Giessen, Germany.
7. Research Institute for Health Sciences and Technologies (SABITA), Medipol University, Istanbul, Turkey.
Abstract
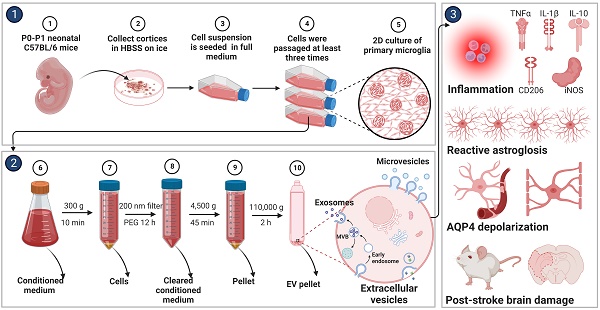
Background: Stroke stimulates reactive astrogliosis, aquaporin 4 (AQP4) depolarization and neuroinflammation. Preconditioned extracellular vesicles (EVs) from microglia exposed to hypoxia, in turn, reduce poststroke brain injury. Nevertheless, the underlying mechanisms of such effects are elusive, especially with regards to inflammation, AQP4 polarization, and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow.
Methods: Primary microglia and astrocytes were exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) injury. For analyzing the role of AQP4 expression patterns under hypoxic conditions, a co-culture model of astrocytes and microglia was established. Further studies applied a stroke model, where some mice also received an intracisternal tracer infusion of rhodamine B. As such, these in vivo studies involved the analysis of AQP4 polarization, CSF flow, astrogliosis, and neuroinflammation as well as ischemia-induced brain injury.
Results: Preconditioned EVs decreased periinfarct AQP4 depolarization, brain edema, astrogliosis, and inflammation in stroke mice. Likewise, EVs promoted postischemic CSF flow and cerebral blood perfusion, and neurological recovery. Under in vitro conditions, hypoxia stimulated M2 microglia polarization, whereas EVs augmented M2 microglia polarization and repressed M1 microglia polarization even further. In line with this, astrocytes displayed upregulated AQP4 clustering and proinflammatory cytokine levels when exposed to OGD, which was reversed by preconditioned EVs. Reduced AQP4 depolarization due to EVs, however, was not a consequence of unspecific inflammatory regulation, since LPS-induced inflammation in co-culture models of astrocytes and microglia did not result in altered AQP4 expression patterns in astrocytes.
Conclusions: These findings show that hypoxic microglia may participate in protecting against stroke-induced brain damage by regulating poststroke inflammation, astrogliosis, AQP4 depolarization, and CSF flow due to EV release.
Keywords: AQP4 polarization, astrogliosis, CSF flow, extracellular vesicles, inflammation, microglia, stroke
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact