13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(15):5183-5206. doi:10.7150/thno.85419 This issue Cite
Review
Aptamer-engineered (nano)materials for theranostic applications
1. Centre for Molecular Medicine and Innovative Therapeutics, Health Futures Institute, Murdoch University, Perth, WA 6150, Australia.
2. Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Science, Perth, WA 6009, Australia.
3. Student Research Committee, Department of Medical Biotechnology, School of Advanced Technologies in Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
4. Cellular and Molecular Biology Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Abstract
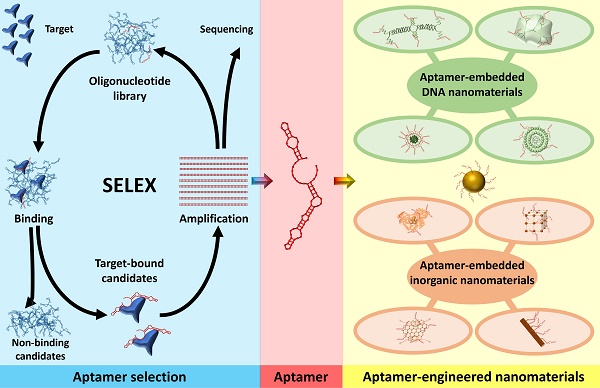
A diverse array of organic and inorganic materials, including nanomaterials, has been extensively employed in multifunctional biomedical applications. These applications encompass drug/gene delivery, tissue engineering, biosensors, photodynamic and photothermal therapy, and combinatorial sciences. Surface and bulk engineering of these materials, by incorporating biomolecules and aptamers, offers several advantages such as decreased cytotoxicity, improved stability, enhanced selectivity/sensitivity toward specific targets, and expanded multifunctional capabilities. In this comprehensive review, we specifically focus on aptamer-modified engineered materials for diverse biomedical applications. We delve into their mechanisms, advantages, and challenges, and provide an in-depth analysis of relevant literature references. This critical evaluation aims to enhance the scientific community's understanding of this field and inspire new ideas for future research endeavors.
Keywords: nanomaterials, aptamer, aptamer modified materials, biosensors, biomedical engineering
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact