13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(15):5247-5265. doi:10.7150/thno.88998 This issue Cite
Review
The role of radiolabeling in BNCT tracers for enhanced dosimetry and treatment planning
1. Division of Applied RI, Korea Institute of Radiological & Medical Sciences (KIRAMS) Seoul 01812, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Nuclear Engineering, Pakistan Institute of Engineering and Applied Sciences, P. O. Nilore, Islamabad 45650, Pakistan.
Abstract
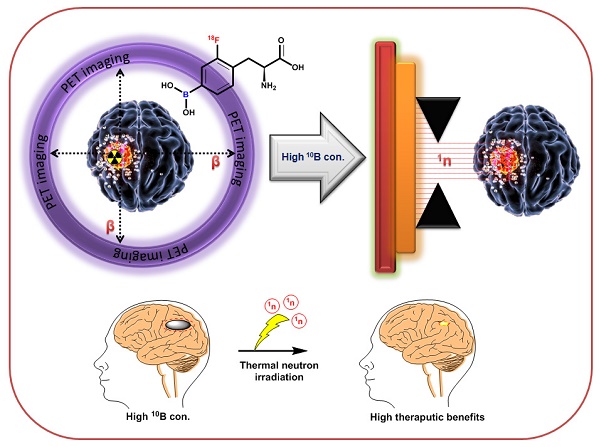
Positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) are potent technologies for non-invasive imaging of pharmacological and biochemical processes in both preclinical and advanced clinical research settings. In the field of radiation therapy, boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) stands out because it harnesses biological mechanisms to precisely target tumor cells while preserving the neighboring healthy tissues. To achieve the most favorable therapeutic outcomes, the delivery of boron-enriched tracers to tumors must be selective and efficient, with a substantial concentration of boron atoms meticulously arranged in and around the tumor cells. Although several BNCT tracers have been developed to facilitate the targeted and efficient delivery of boron to tumors, only a few have been labeled with PET or SPECT radionuclides. Such radiolabeling enables comprehensive in vivo examination, encompassing crucial aspects such as pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, tumor selectivity, and accumulation and retention of the tracer within the tumor. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the essential aspects of BNCT tracers, focusing on their radiolabeling with PET or SPECT radioisotopes. This leads to more effective and targeted treatment approaches which ultimately enhance the quality of patient care with respect to cancer treatment.
Keywords: BNCT, PET, SPECT, radiolabeling, theranostics, targeted therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact