13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2023; 13(15):5386-5417. doi:10.7150/thno.87854 This issue Cite
Review
Stimuli-activatable nanomedicine meets cancer theranostics
1. Department of Radiology, and Department of Geriatrics, Laboratory of Heart Valve Disease, Huaxi MR Research Center (HMRRC), Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology, National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics, Frontiers Science Center for Disease-Related Molecular Network, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, No. 37 Guoxue Alley, Chengdu 610041, China.
2. Functional and Molecular Imaging Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province and Research Unit of Psychoradiology, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Chengdu 610041, China
3. Department of Radiology, West China Xiamen Hospital of Sichuan University, 699 Jinyuan Xi Road, Jimei District, 361021 Xiamen, Fujian, China.
*Those authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
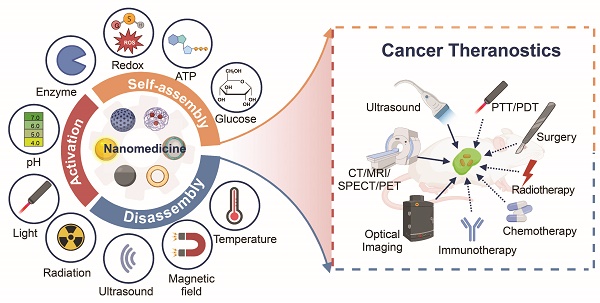
Stimuli-activatable strategies prevail in the design of nanomedicine for cancer theranostics. Upon exposure to endogenous/exogenous stimuli, the stimuli-activatable nanomedicine could be self-assembled, disassembled, or functionally activated to improve its biosafety and diagnostic/therapeutic potency. A myriad of tumor-specific features, including a low pH, a high redox level, and overexpressed enzymes, along with exogenous physical stimulation sources (light, ultrasound, magnet, and radiation) have been considered for the design of stimuli-activatable nano-medicinal products. Recently, novel stimuli sources have been explored and elegant designs emerged for stimuli-activatable nanomedicine. In addition, multi-functional theranostic nanomedicine has been employed for imaging-guided or image-assisted antitumor therapy. In this review, we rationalize the development of theranostic nanomedicine for clinical pressing needs. Stimuli-activatable self-assembly, disassembly or functional activation approaches for developing theranostic nanomedicine to realize a better diagnostic/therapeutic efficacy are elaborated and state-of-the-art advances in their structural designs are detailed. A reflection, clinical status, and future perspectives in the stimuli-activatable nanomedicine are provided.
Keywords: exogenous stimuli, Endogenous stimuli, stimuli activation, nanomedicine, cancer theranostics
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact