13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(2):622-639. doi:10.7150/thno.88759 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Pharmacological inhibition of MYC to mitigate chemoresistance in preclinical models of squamous cell carcinoma
Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Peking University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China. National Center of Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & National Engineering Laboratory for Digital and Material Technology of Stomatology, Beijing 100081, China.
#Shuo Liu and Zhen Qin contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
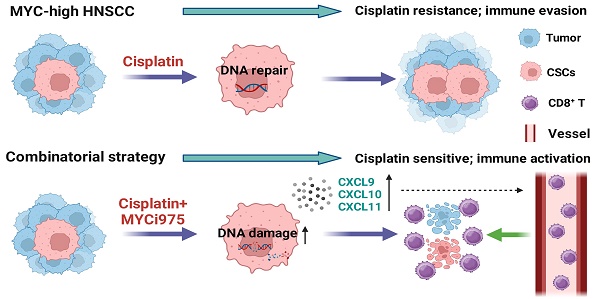
Rationale: Cisplatin-based chemotherapy is the first-line treatment for late-stage head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, resistance to cisplatin has become a major obstacle for effective therapy. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are critical for tumor initiation, growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance. How to effectively eliminate CSCs and overcome chemoresistance remains a key challenge. Herein, we confirmed that MYC plays critical roles in chemoresistance, and explored targeting MYC to overcome cisplatin resistance in preclinical models.
Methods: The roles of MYC in HNSCC cisplatin resistance and cancer stemness were tested in vitro and in vivo. The combined therapeutic efficiency of MYC targeting using the small molecule MYC inhibitor MYCi975 and cisplatin was assessed in a 4‑nitroquinoline 1-oxide-induced model and in a patient-derived xenograft model.
Results: MYC was highly-expressed in cisplatin-resistant HNSCC. Targeting MYC using MYCi975 eliminated CSCs, prevented metastasis, and overcame cisplatin resistance. MYCi975 also induced tumor cell-intrinsic immune responses, and promoted CD8+ T cell infiltration. Mechanistically, MYCi975 induced the DNA damage response and activated the cGAS-STING-IRF3 signaling pathway to increase CD8+ T cell-recruiting chemokines.
Conclusions: Our findings suggested that targeting MYC might eliminate CSCs, prevent metastasis, and activate antitumor immunity to overcome cisplatin resistance in HNSCC.
Keywords: Cisplatin resistance, Cancer stem cells, MYC, Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, DNA damage response
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact