13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(2):892-910. doi:10.7150/thno.87962 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Reciprocal interactions between malignant cells and macrophages enhance cancer stemness and M2 polarization in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Pathology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
2. State Key Laboratory of Liver Research, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
3. Department of Pathology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong.
4. Department of Surgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hong Kong.
5. Department of Surgery, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
#These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
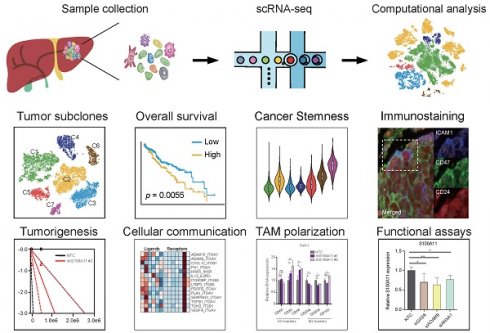
Background: The tumor microenvironment of cancers has emerged as a crucial component in regulating cancer stemness and plays a pivotal role in cell-cell communication. However, the specific mechanisms underlying these phenomena remain poorly understood.
Methods: We performed the single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) on nine HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients. The heterogeneity of the malignant cells in pathway functions, transcription factors (TFs) regulation, overall survival, stemness, as well as ligand-receptor-based intercellular communication with macrophages were characterized. The aggressive and stemness feature for the target tumor subclone was validated by the conduction of in vitro assays including sphere formation, proliferation, Annexin V apoptosis, flow cytometry, siRNA library screening assays, and multiple in vivo preclinical mouse models including mouse hepatoma cell and human HCC cell xenograft models with subcutaneous or orthotopic injection.
Results: Our analysis yielded a comprehensive atlas of 31,664 cells, revealing a diverse array of malignant cell subpopulations. Notably, we identified a stemness-related subclone of HCC cells with concurrent upregulation of CD24, CD47, and ICAM1 expression that correlated with poorer overall survival. Functional characterization both in vitro and in vivo validated S100A11 as one of the top downstream mediators for tumor initiation and stemness maintenance of this subclone. Further investigation of cell-cell communication within the tumor microenvironment revealed a propensity for bi-directional crosstalk between this stemness-related subclone and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs). Co-culture study showed that this interaction resulted in the maintenance of the expression of cancer stem cell markers and driving M2-like TAM polarization towards a pro-tumorigenic niche. We also consolidated an inverse relationship between the proportions of TAMs and tumor-infiltrating T cells.
Conclusions: Our study highlighted the critical role of stemness-related cancer cell populations in driving an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and identified the S100A11 gene as a key mediator for stemness maintenance in HCC. Moreover, our study provides support that the maintenance of cancer stemness is more attributed to M2 polarization than the recruitment of the TAMs.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Single-cell RNA sequencing, Cancer stem cell, Tumor heterogeneity, Macrophage polarization
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact