13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2024; 14(7):2897-2914. doi:10.7150/thno.90608 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Adaptive plasticity of natural interleukin-35-induced regulatory T cells (Tr35) that are required for T-cell immune regulation
1. Center of Biotherapy, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, P.R. China.
2. CAS Key Laboratory of Pathogenic Microbiology and Immunology, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Beijing 100101, P.R. China.
3. Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Guangxi Nanning, P.R. China.
4. Department of General Surgery, Beijing Hospital, National Center of Gerontology; Institute of Geriatric Medicine, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100730, P.R. China.
5. National Cancer Center/National Clinical Research Center for Cancer/Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, 100021, P.R. China.
6. Savaid Medical School, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 101408, P.R. China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
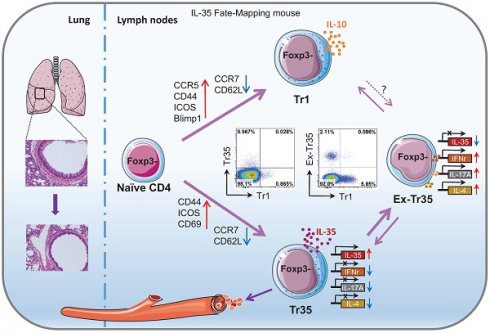
Background: IL-35 potently inhibits immune responses both in vivo and in vitro. However, the specific characteristics of IL-35-producing cells, including their developmental origin, cellular phenotype, and function, are unknown.
Methods: By using a novel IL-35 reporter mouse (Ebi3-Dre-Thy1.1) and double transgenic fate-mapping reporter mice (35EbiT-Rosa26-rox-tdTomato reporter mice or Foxp3 fate-mapping system), we tracked and analyzed the differentiation and developmental trajectories of Tr35 cells in vivo. And then we investigated the therapeutic effects of OVA-specific Tr35 cells in an OVA-induced allergic airway disease model.
Results: We identified a subset of cells, denoted Tr35 cells, that secrete IL-35 but do not express Foxp3. These cells have high expression of molecules associated with T-cell activation and can inhibit T-cell proliferation in vitro. Our analyses showed that Tr35 cells are a distinct subpopulation of cells that are independent of Tr1 cells. Tr35 cells exhibit a unique gene expression profile and tissue distribution. The presence of Thy1.1 (Ebi3) expression in Tr35 cells indicates their active secretion of IL-35. However, the proportion of ex-Tr35 cells (Thy1.1-) is significantly higher compared to Tr35 cells (Thy1.1+). This suggests that Tr35 cells possess the ability to regulate IL-35 expression rapidly in vivo. Tr35 cells downregulated the expression of the inflammatory cytokines IL-4, IFN-γ and IL-17A. However, once Tr35 cells lost IL-35 expression and became exTr35 cells, the expression of inflammatory cytokines was upregulated. Importantly, our findings indicate that Tr35 cells have therapeutic potential. In an OVA-induced allergic airway disease mouse model, Tr35 cell reinfusion significantly reduced airway hyperresponsiveness and histopathological airway and lung inflammation.
Conclusions: We have identified a subset of Tregs, Tr35 cells, that are distinct from Tr1 cells. Tr35 cells can dynamically regulate the secretion of inflammatory cytokines by controlling IL-35 expression to regulate inflammatory immune responses.
Keywords: induced Treg, interleukin-35, Tr35 trajectory, transgenic reporter mice
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact