13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2014; 4(4):336-365. doi:10.7150/thno.7851 This issue Cite
Review
PI3K-AKT-mTOR-Signaling and beyond: the Complex Network in Gastroenteropancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms
1. Medizinische Klinik 1 CBF, Dept. of Gastroenterology, Infectious Diseases, Rheumatology CC13, Charité Berlin, Germany;
2. Freie Universität Berlin, Institute for Chemistry and Biochemistry, Berlin, Germany;
3. Department of Hematology and Internal Oncology and Center for Neuroendocrine Tumours Bad Berka - ENETS Center of Excellence, Zentralklinik Bad Berka, Germany.
Abstract
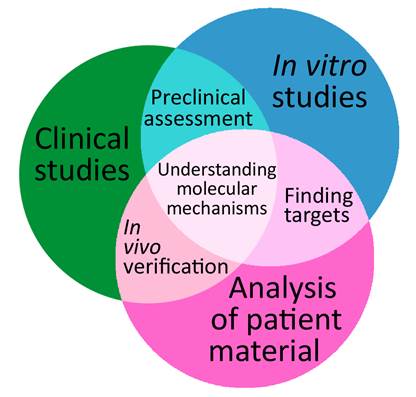
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms are heterogeneous in their clinical behavior and require therapies specially tailored according to staging, grading, origin and expression of peptide receptors. Despite extensive scientific efforts, the therapy options are still not satisfactory. The main reasons are due to the lack of a broad mechanistic knowledge, an insufficient classification of specific diagnostic sub-groups, and predictive markers. GEP-NEN tumors evade early diagnosis because of slow asymptomatic growth behavior and are frequently not detected until metastasized. How signaling networks contribute to tumor progression and how these networks interact remains unclear in large parts. In this review we summarize the knowledge on the growth factor responsive non-angiogenetic pathways in sporadic GEP-NENs, highlight promising mechanistic research approaches, and describe important therapy targets.
Keywords: Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms, signal transduction, growth factors, kinases, biotherapy, molecular biology, inhibitor.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact