13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2015; 5(4):418-430. doi:10.7150/thno.10020 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Detection of High-Risk Atherosclerotic Plaques with Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Receptor on Activated Platelets
State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, Department of Cardiology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.
Abstract
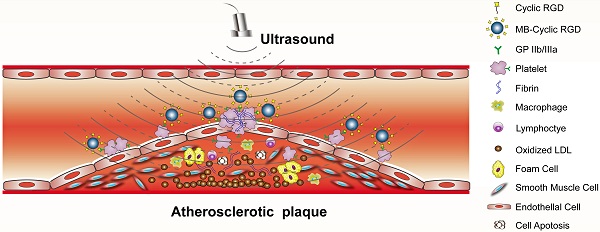
Objective: Ultrasound molecular imaging (UMI) of glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor on activated platelets offers a unique means of identifying high-risk atherosclerosis. We hypothesized that contrast-enhanced ultrasound with microbubbles (MBs) targeted to GP IIb/IIIa could be used to detect and quantify activated platelets on the surface of advanced plaques.
Methods and Results: A mouse model of advanced atherosclerosis was generated by maintaining apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/-) mice on a hypercholesterolemic diet (HCD). The three other experimental groups consisted of ApoE-/- and wild-type (C57BL/6) mice fed a normal chow diet and C57BL/6 mice on an HCD diet. Plaque formation was confirmed by histological and immunohistochemical methods using light, fluorescence, and electron microscopy. Mice were injected with a lipid MB-conjugated cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp peptide or nonspecific control peptide, and the abdominal aorta was examined by UMI. The accumulation of GP IIb/IIIa and activated platelets on the surface of atherosclerotic plaques was highest in the ApoE-/-+HCD group, followed by ApoE-/-+chow, C57BL/6+HCD, and C57BL/6+chow groups (P<0.05). Notably, GP IIb/IIIa expression was associated with the vulnerability index and necrotic center/fiber cap ratio (P<0.05), and contrast video intensity from adhered cyclic Arg-Gly-Asp-modified MBs (MB-cRGDs) was correlated with GP IIb/IIIa expression on the plaque surface (P<0.05).
Conclusion: GP IIb/IIIa of activated platelets on the atherosclerotic endothelium is a biomarker for high-risk plaques that can be quantified by UMI using MB-cRGDs, providing a noninvasive means for detecting high-risk plaques and preventing acute cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis, Microbubbles, Molecular imaging, Platelets, Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact