13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(9):1306-1323. doi:10.7150/thno.14858 This issue Cite
Review
The Smart Drug Delivery System and Its Clinical Potential
State Key Laboratory of Bioelectronics, Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Biomaterials and Devices, School of Biomedical Sciences and Medical Engineering, Southeast University, Nanjing, 210009, China.
Abstract
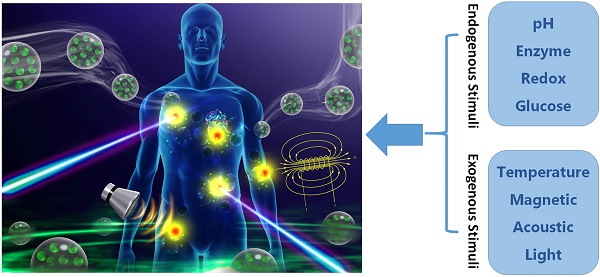
With the unprecedented progresses of biomedical nanotechnology during the past few decades, conventional drug delivery systems (DDSs) have been involved into smart DDSs with stimuli-responsive characteristics. Benefiting from the response to specific internal or external triggers, those well-defined nanoplatforms can increase the drug targeting efficacy, in the meantime, reduce side effects/toxicities of payloads, which are key factors for improving patient compliance. In academic field, variety of smart DDSs have been abundantly demonstrated for various intriguing systems, such as stimuli-responsive polymeric nanoparticles, liposomes, metals/metal oxides, and exosomes. However, these nanoplatforms are lack of standardized manufacturing method, toxicity assessment experience, and clear relevance between the pre-clinical and clinical studies, resulting in the huge difficulties to obtain regulatory and ethics approval. Therefore, such relatively complex stimulus-sensitive nano-DDSs are not currently approved for clinical use. In this review, we highlight the recent advances of smart nanoplatforms for targeting drug delivery. Furthermore, the clinical translation obstacles faced by these smart nanoplatforms have been reviewed and discussed. We also present the future directions and perspectives of stimuli-sensitive DDS in clinical applications.
Keywords: Controlled release, Smart nanoplatform, Drug delivery system (DDS), Biomaterials, Nanomedicine.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact