13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2016; 6(11):1821-1832. doi:10.7150/thno.15311 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Potentiation of Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy by the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib
1. Department of Molecular Genetics, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
2. Department of Radiology & Nuclear Medicine, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
3. Department of Radiation Oncology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
4. Department of Surgery, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
5. Department of Pathology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, The Netherlands
Abstract
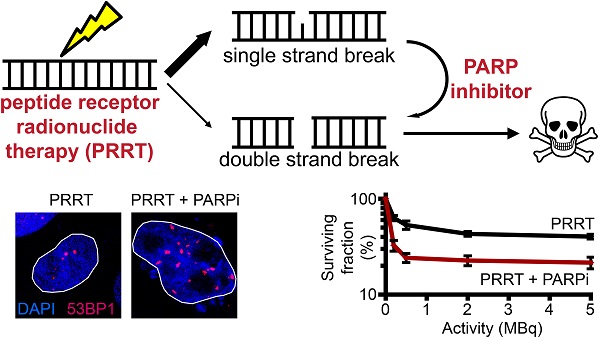
Metastases expressing tumor-specific receptors can be targeted and treated by binding of radiolabeled peptides (peptide receptor radionuclide therapy or PRRT). For example, patients with metastasized somatostatin receptor-positive neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) can be treated with radiolabeled somatostatin analogues, resulting in strongly increased progression-free survival and quality of life. There is nevertheless still room for improvement, as very few patients can be cured at this stage of disease. We aimed to specifically sensitize replicating tumor cells without further damage to healthy tissues. Thereto we investigated the DNA damaging effects of PRRT with the purpose to enhance these effects through modulation of the DNA damage response. Although PRRT induces DNA double strand breaks (DSBs), a larger fraction of the induced lesions are single strand breaks (expected to be similar to those induced by external beam radiotherapy) that require poly-[ADP-ribose]-polymerase 1 (PARP-1) activity for repair. If these breaks cannot be repaired, they will cause replication fork arrest and DSB formation during replication. Therefore, we used the PARP-1 inhibitor Olaparib to increase the number of cytotoxic DSBs. Here we show that this new combination strategy synergistically sensitized somatostatin receptor expressing cells to PRRT. We observed increased cell death and reduced cellular proliferation compared to the PRRT alone. The enhanced cell death was caused by increased numbers of DSBs that are repaired with remarkably slow kinetics, leading to genome instability. Furthermore, we validated the increased DSB induction after PARP inhibitor addition in the clinically relevant model of living human NET slices. We expect that this combined regimen can thus augment current PRRT outcomes.
Keywords: Neuroendocrine tumors, somatostatin receptor, peptide receptor radionuclide therapy, 177Lu-DOTA-[Tyr3]octreotate, DNA damage response, combination treatment, PARP inhibitor
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact