13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(1):106-116. doi:10.7150/thno.16911 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Heparin improves BMSC cell therapy: Anticoagulant treatment by heparin improves the safety and therapeutic effect of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell cytotherapy
1. State Key Laboratory of Military Stomatology & National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases & Shaanxi International Joint Research Center for Oral Diseases, Center for Tissue Engineering, School of Stomatology, The Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China;
2. Research and Development Center for Tissue Engineering, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China;
3. Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Jia Mu Si University, JiaMuSi, Heilongjiang 154007, China;
4. Department of Orthodontics, Stomatology Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University College of Medicine, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China;
5. Chinese Association of Plastics and Aesthetics, Beijing 100039, China;
6. Department of Otolaryngology, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi'an, Shaanxi 710032, China.
Abstract
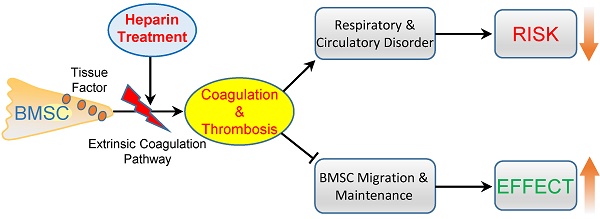
Systemic infusion of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) has become a promising strategy for disease treatment and tissue regeneration. Strategies to enhance the efficiency of BMSC cell therapy are crucial to promote its clinical application. Here, we aimed to improve BMSC cell therapy by inhibiting the BMSC-induced coagulation reaction. Intravenous injection of gradient BMSCs into mice showed that BMSCs were not fully compatible with blood. Large doses of BMSCs induced a series of symptoms of respiratory failure and heart failure. Histological and homeostasis analysis confirmed that large doses of BMSCs induced disseminated intravascular thrombosis, exhaustion of platelets and coagulation factors, and prolonged prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT). Similar to mouse BMSCs, goat and human BMSCs also induced coagulation reactions in vitro and in vivo. The coagulation was induced mostly by tissue factor, the overexpression of which enhanced the procoagulant activity of BMSCs during in vitro culture. Notably, clinical doses of BMSCs in cell therapy also induced mild and reversible coagulation, which increased BMSC lung embolism and clearance. Anticoagulation treatment by heparin (400 U/kg) prevented BMSC-induced coagulation and the acute adverse effects of large-dose BMSCs infusion efficiently. Importantly, heparin treatment led to decreased BMSC lung embolism and enhanced migration and maintenance of BMSCs to target organs in cell therapy. Based on an experimental colitis model, we confirmed that heparin treatment enhanced the effect of BMSC therapy efficiently to reduce mortality, prevent weight loss, suppress inflammation reaction and alleviate tissue injury. In conclusion, BMSCs possess procoagulant activity that could induce disseminated coagulation and thrombosis in recipients. Anticoagulation treatment by heparin is a practical strategy to improve both the safety and therapeutic effect of BMSC therapy.
Keywords: Anticoagulant, Cell therapy, Coagulation, Heparin, Mesenchymal stem cell.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact