13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(2):253-269. doi:10.7150/thno.16681 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Enhancing Nanoparticle Accumulation and Retention in Desmoplastic Tumors via Vascular Disruption for Internal Radiation Therapy
1. Division of Molecular Pharmaceutics and Center for Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery, Eshelman School of Pharmacy, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 27599-7571, USA.
2. UNC and NCSU Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, Chapel Hill, NC 27599.
Abstract
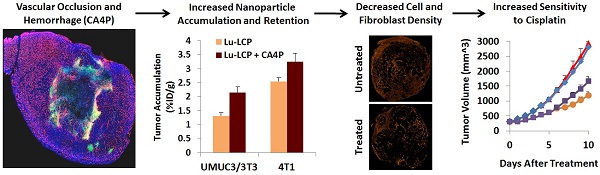
Aggressive, desmoplastic tumors are notoriously difficult to treat because of their extensive stroma, high interstitial pressure, and resistant tumor microenvironment. We have developed a combination therapy that can significantly slow the growth of large, stroma-rich tumors by causing massive apoptosis in the tumor center while simultaneously increasing nanoparticle uptake through a treatment-induced increase in the accumulation and retention of nanoparticles in the tumor. The vascular disrupting agent Combretastatin A-4 Phosphate (CA4P) is able to increase the accumulation of radiation-containing nanoparticles for internal radiation therapy, and the retention of these delivered radioisotopes is maintained over several days. We use ultrasound to measure the effect of CA4P in live tumor-bearing mice, and we encapsulate the radio-theranostic isotope 177Lutetium as a therapeutic agent as well as a means to measure nanoparticle accumulation and retention in the tumor. This combination therapy induces prolonged apoptosis in the tumor, decreasing both the fibroblast and total cell density and allowing further tumor growth inhibition using a cisplatin-containing nanoparticle.
Keywords: Cancer, Theranostic, Nanoparticle, CA4P, EPR, Desmoplastic, Cisplatin.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact