13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(8):2261-2276. doi:10.7150/thno.19091 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeted Delivery to Tumor-associated Pericytes via an Affibody with High Affinity for PDGFRβ Enhances the in vivo Antitumor Effects of Human TRAIL
1. Key Lab of Transplant Engineering and Immunology, MOH, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China;
2. Regenerative Medical Research Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, 610041, China.
* These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
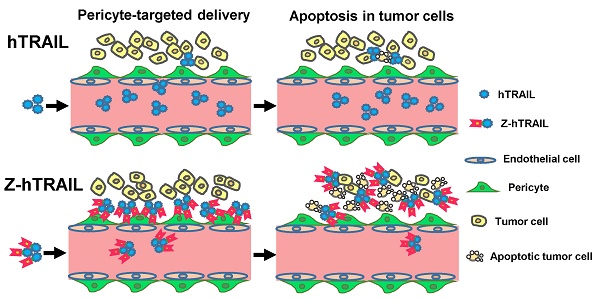
Human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (hTRAIL) has exhibited superior in vitro cytotoxicity in a variety of tumor cells. However, hTRAIL showed a disappointing anticancer effect in clinical trials, although hTRAIL-based regimens were well tolerated. One important reason might be that hTRAIL was largely trapped by its decoy receptors, which are ubiquitously expressed on normal cells. Tumor-targeted delivery might improve the tumor uptake and thus enhance the antitumor effect of hTRAIL. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor β (PDGFRβ)-expressing pericytes are enriched in tumor tissues derived both from patients with colon cancer and from mice bearing colorectal tumor xenografts. A ZPDGFRβ affibody showed high affinity (nM) for PDGFRβ and was predominantly distributed on tumor-associated PDGFRβ-positive pericytes. Co-administration with the ZPDGFRβ affibody did not significantly enhance the antitumor effect of hTRAIL in mice bearing tumor xenografts. Fusion to the ZPDGFRβ affibody endows hTRAIL with PDGFRβ-binding ability but does not interfere with its death receptor binding and activation. The fused ZPDGFRβ affibody mediated PDGFRβ-dependent binding of hTRAIL to pericytes. In addition, hTRAIL bound on pericytes could kill tumor cells through juxtatropic activity or exhibit cytotoxicity in tumor cells after being released from pericytes. Intravenously injected hTRAIL fused to ZPDGFRβ affibody initially accumulated on tumor-associated pericytes and then diffused to the tumor parenchyma over time. Fusion to the ZPDGFRβ affibody increased the tumor uptake of hTRAIL, thus enhancing the antitumor effect of hTRAIL in mice bearing tumor xenografts. These results demonstrate that pericyte-targeted delivery mediated by a ZPDGFRβ affibody is an alternative strategy for tumor-targeted delivery of anticancer agents.
Keywords: Pericyte, Platelet-derived growth factor receptor, Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand, Affibody, Drug delivery, Cancer therapy.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact