13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(9):2431-2442. doi:10.7150/thno.19184 This issue Cite
Research Paper
3-D Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Mapping of Arteries to Detect Metabolically Active but Angiographically Invisible Atherosclerotic Lesions
1. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles, California;
2. Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles, California;
3. Veterans Affairs West Los Angeles Medical Center, Los Angeles, California;
4. Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, California;
5. Department of Bioengineering, Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, California.
* Equal contribution
Abstract
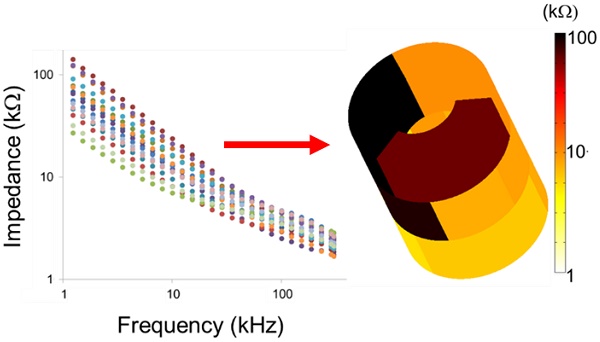
We designed a novel 6-point electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) sensor with 15 combinations of permutations for the 3-D mapping and detection of metabolically active atherosclerotic lesions. Two rows of 3 stretchable electrodes circumferentially separated by 120° were mounted on an inflatable balloon for intravascular deployment and endoluminal interrogation. The configuration and 15 permutations of 2-point EIS electrodes allowed for deep arterial penetration via alternating current (AC) to detect varying degrees of lipid burden with distinct impedance profiles (Ω). By virtue of the distinctive impedimetric signature of metabolically active atherosclerotic lesions, a detailed impedance map was acquired, with the 15 EIS permutations uncovering early stages of disease characterized by fatty streak lipid accumulation in the New Zealand White rabbit model of atherosclerosis. Both the equivalent circuit and statistical analyses corroborated the 3-D EIS permutations to detect small, angiographically invisible, lipid-rich lesions, with translational implications for early atherosclerotic disease detection and prevention of acute coronary syndromes or strokes.
Keywords: Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, 3-D Mapping, Atherosclerosis.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact