13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(19):4689-4698. doi:10.7150/thno.21672 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CO2-based amphiphilic polycarbonate micelles enable a reliable and efficient platform for tumor imaging
1. State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130022, China
2. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3. Department Key Laboratory of Polymer Ecomaterials, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changchun 130022, China
4. Department of Radiology, Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, 130041, China
Abstract
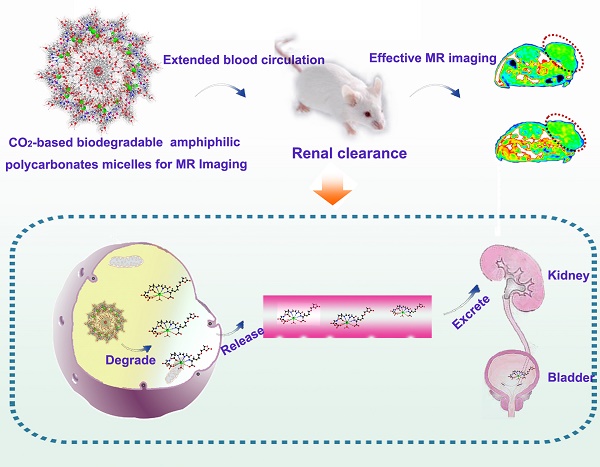
Biodegradable polymeric nanomaterials can be directly broken down by intracellular processes, offering a desirable way to solve toxicity issues for cancer diagnosis and treatment. Among them, aliphatic polycarbonates are approved for application in biological fields by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA), however, high hydrophobicity, deficient functionality and improper degradation offer significant room for improvement in these materials. Methods: To achieve progress in this direction, herein, we demonstrate that CO2-based amphiphilic polycarbonates (APC) with improved hydrophilicity and processability can be used as a reliable and efficient platform for tumor imaging. To better investigate their potential, we devised a convenient strategy through conjugation of APC with gadolinium (Gd). Results: The resulting polymeric micelles (APC-DTPA/Gd) exhibit excellent magnetic resonance imaging performance, simultaneously enabling real-time visualization of bioaccumulation and decomposition of polymeric micelles in vivo. Importantly, these micelles can be degraded to renally cleared products within a reasonable timescale without evidence of toxicity. Conclusion: Our findings may help the development of CO2-based amphiphilic polycarbonate for cancer diagnosis and treatment, accompanied by their low-toxicity degradation pathway.
Keywords: carbon dioxide, polycarbonate, biodegradable, renal clearance, imaging agents
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact