13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2017; 7(19):4825-4835. doi:10.7150/thno.21815 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Changing Therapeutic Role of Chemo-radiotherapy for Loco-regionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma from Two/Three-Dimensional Radiotherapy to Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy: A Network Meta-Analysis
1. Department of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China
2. Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center; Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China
3. State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, National Clinical Research Center for Kidney Disease, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China;
4. Department of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, 510515, China;
5. Department of Radiation Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, 651 Dongfeng East Road, Guangzhou 510060, P. R. China
6. Department of Cancer Prevention, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, P. R. China
7. Department of Radiotherapy, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, P. R. China
8. Department of Medical Statistics and Epidemiology, School of Public Health, Sun Yat-sen University, 74 Zhongshan Second Road, Guangzhou 510080, P. R. China
9. Department of Clinical Trial Center, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, P. R. China
#Rui You, Ying-Shu Cao, Pei-Yu Huang, Lei Chen, Qi Yang contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
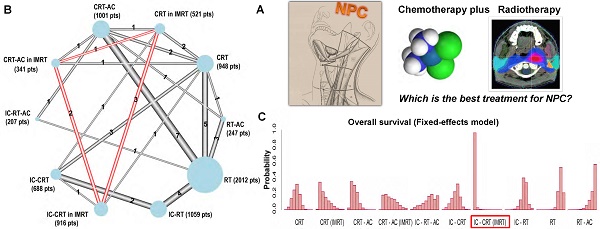
Purpose: We used randomized trials of radiotherapy (RT) with or without chemotherapy in non-metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma to investigate the survival benefit of chemoradiotherapy regimens between two/three-dimensional radiotherapy (2D/3D RT) and intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT).
Methods: Overall, 27 trials and 7,940 patients were included. Treatments were grouped into seven categories including RT alone, induction chemotherapy (IC) followed by RT (IC-RT), RT followed by adjuvant chemotherapy (RT-AC), IC followed by RT followed by AC (IC-RT-AC), concurrent chemo-radiotherapy (CRT), IC followed by CRT (IC-CRT), and CRT followed by AC (CRT-AC). To distinguish between 2D/3D RT and IMRT, three categories in IMRT were newly added, including CRT in IMRT, IC-CRT in IMRT, and CRT-AC in IMRT. The P score was used to rank the treatments.
Results: Both fixed- and random-effects frequentist and Bayesian network meta-analysis models were applied, which provided similar results and the same ranking. IC-CRT was the most effective regimen compared with CRT-AC and CRT in the IMRT era for overall survival (OS) (HR, 95% CI, IC-CRT vs. CRT-AC, 0.61 (0.45, 0.82); IC-CRT vs. CRT 0.65 (0.47, 0.91)), progression-free survival (PFS) (0.69 (0.54, 0.88); 0.63 (0.49, 0.80)), and distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS) (0.58 (0.28, 1.21); 0.60 (0.42, 0.85)). CRT-AC achieved the highest survival benefit compared with CRT, and IC-CRT for loco-regional relapse-free survival (LRRFS) (0.44 (0.15, 1.28); 0.72 (0.22, 2.33)). Among these 10 categories, after distinguishing between 2D/3D RT and IMRT, IC-CRT in IMRT ranked first for OS, PFS, and DMFS, and CRT-AC in IMRT ranked first for LRRFS.
Conclusion: IC-CRT should be the most suitable regimen for loco-regionally advanced NPC in the IMRT era.
Keywords: nasopharyngeal carcinoma, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy, survival outcome, network meta-analysis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact