13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(14):3737-3750. doi:10.7150/thno.25487 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Blocking CDK1/PDK1/β-Catenin signaling by CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 increased the efficacy of sorafenib treatment by targeting cancer stem cells in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma
1. Department of Surgery, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
2. Department of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong.
Abstract
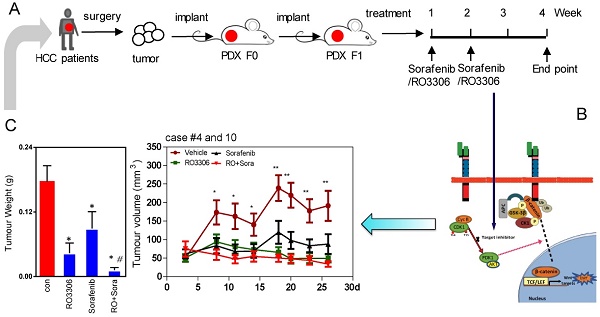
Rationale: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignant solid tumor wherein CDK1/PDK1/β-Catenin is activated, suggesting that inhibition of this pathway may have therapeutic potential.
Methods: CDK1 overexpression and clinicopathological parameters were analyzed. HCC patient-derived xenograft (PDX) tumor models were treated with RO3306 (4 mg/kg) or sorafenib (30 mg/kg), alone or in combination. The relevant signaling of CDK1/PDK1/β-Catenin was measured by western blot. Silencing of CDK1 with shRNA and corresponding inhibitors was performed for mechanism and functional studies.
Results: We found that CDK1 was frequently augmented in up to 46% (18/39) of HCC tissues, which was significantly associated with poor overall survival (p=0.008). CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 in combination with sorafenib treatment significantly decreased tumor growth in PDX tumor models. Furthermore, the combinatorial treatment could overcome sorafenib resistance in the HCC case #10 PDX model. Western blot results demonstrated the combined administration resulted in synergistic down-regulation of CDK1, PDK1 and β-Catenin as well as concurrent decreases of pluripotency proteins Oct4, Sox2 and Nanog. Decreased CDK1/PDK1/β-Catenin was associated with suppression of epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT). In addition, a low dose of RO3306 and sorafenib combination could inhibit 97H CSC growth via decreasing the S phase and promoting cells to enter into a Sub-G1 phase. Mechanistic and functional studies silencing CDK1 with shRNA and RO3306 combined with sorafenib abolished oncogenic function via downregulating CDK1, with downstream PDK1 and β-Catenin inactivation.
Conclusion: Anti-CDK1 treatment can boost sorafenib antitumor responses in PDX tumor models, providing a rational combined treatment to increase sorafenib efficacy in the clinic.
Keywords: cancer stem cells, hepatocellular carcinoma, PDX models, CDK1 inhibitor, RO3306, sorafenib
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact