13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2018; 8(16):4447-4461. doi:10.7150/thno.24284 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Aspirin cooperates with p300 to activate the acetylation of H3K9 and promote FasL-mediated apoptosis of cancer stem-like cells in colorectal cancer
1. Department of Surgical Oncology, Second Affiliated Hospital and Cancer Institute (Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention & Intervention, National Ministry of Education, Provincial Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Medical Sciences), Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
2. Department of Neuroscience, Tufts University School of Medicine; Programs of Neuroscience and Cellular, Molecular and Development Biology, Tufts Sackler School of Graduate Biomedical Sciences, Boston, MA, USA
3. Department of Pharmacy, Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
4. Department of Gastroenterology, Second Affiliated Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou, China
5. College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
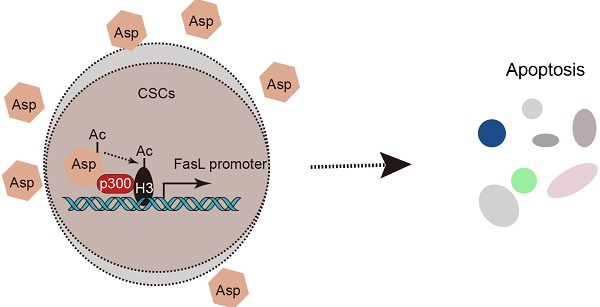
Cancer stem-like cells (CSCs) have been proposed as a key driving force of tumor growth and relapse in colorectal cancer (CRC), and therefore, they are promising targets for cancer therapy. Epidemiological evidence has suggested that the daily use of aspirin reduces overall mortality of CRC and the risk of distant metastasis. We investigated the effect and mechanism of aspirin on CSCs in CRC.
Methods: The ratio of CSCs was analyzed after aspirin treatment both in a cell model and patient samples. Chemically modified aspirin and immunoprecipitation were adopted to detect the target proteins of aspirin. A locus-specific light-inducible epigenetic modification system based on CRISPR technology was constructed to verify the causal relationship in these molecular events. In vivo characterization was performed in a xenograft model.
Results: We found that aspirin induces apoptosis in enriched colorectal CSCs, inhibits tumor progression, and enhances the anti-neoplastic effects of chemotherapeutic agents. Furthermore, aspirin directly interacts with p300 in the nucleus, promotes H3K9 acetylation, activates FasL expression, and induces apoptosis in colorectal CSCs. Notably, these effects of aspirin are absent in non-CSCs since H3K9 is hypermethylated in non-CSCs and the effects are not induced by other NSAIDs. In addition, aspirin can suppress oxaliplatin-enriched CSCs and serve as an adjuvant therapy.
Conclusions: Taken together, we revealed a unique epigenetic and cox-independent pathway (p300-AcH3K9-FasL axis) by which aspirin eliminates colorectal CSCs. These findings establish an innovative framework of the therapeutic significance of aspirin.
Keywords: Aspirin, FasL, apoptosis, cancer stem-like cells, colorectal cancer
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact