13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(5):1323-1335. doi:10.7150/thno.31079 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Nanoliposomes Co-Encapsulating CT Imaging Contrast Agent and Photosensitizer for Enhanced, Imaging Guided Photodynamic Therapy of Cancer
1. Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518060, P.R. China
2. Bioimaging Core, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Macau, Avenida da Universidade, Taipa, Macau SAR 999078, P.R. China
Abstract
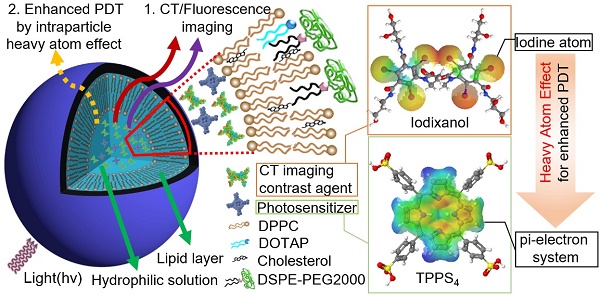
Fluorescence (FL) and X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging-guided photodynamic therapy (PDT) can provide a powerful theranostic tool to visualize, monitor, and treat cancer and other diseases with enhanced accuracy and efficacy.
Methods: In this study, clinically approved iodinated CT imaging contrast agent (CTIA) iodixanol and commercially available photosensitizer (PS) meso-tetrakis (4-sulphonatophenyl) porphine (TPPS4) were co-encapsulated in biocompatible PEGylated nanoliposomes (NL) for enhanced anticancer PDT guided by bimodal (FL and CT) imaging.
Results: The NL co-encapsulation of iodixanol and TPPS4 (LIT) lead to an increase in singlet oxygen generation by PS via the intraparticle heavy-atom (iodine) effect on PS molecules, as it was confirmed by both direct and indirect measurements of singlet oxygen production. The confocal imaging and PDT of cancer cells were performed in vitro, exhibiting the cellular uptake of TPPS4 formulations and enhanced PDT efficacy of LIT. Meanwhile, bimodal (FL and CT) imaging was also conducted with tumor-bearing mice and the imaging results manifested high-efficient accumulation and retention of LIT in tumors. Moreover, PDT of tumor in vivo was shown to be drastically more efficient with LIT than with other formulations of TPPS4.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that LIT can serve as a highly efficient theranostic nanoplatform for enhanced anticancer PDT guided by bimodal (FL and CT) imaging.
Keywords: liposome, computed tomography, fluorescence bioimaging, photodynamic therapy, heavy atom effect
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact