13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(12):3541-3554. doi:10.7150/thno.32908 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Polo-Like Kinase 1 phosphorylates and stabilizes KLF4 to promote tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
1. State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis and Therapy, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
2. Department of VIP Inpatient, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
3. Department of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, China
*Equally contributing first authors
Abstract
Rationale: Advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is an aggressive disease with no targeted therapies and poor outcomes. New innovative targets are urgently needed. KLF4 has been extensively studied in the context of tumors, and current data suggest that it can act as either a tissue-specific tumor-inhibiting or a tumor-promoting gene. Here, we found that KLF4 played as a tumor-promoting gene in NPC, and could be mediated by PLK1.
Methods: Tissue immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay was performed to identify the role of KLF4 in NPC. Global gene expression experiments were performed to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying KLF4-dependent tumorigenesis. Small-molecule kinase inhibitor screening was performed to identify potential upstream kinases of KLF4. The pharmacologic activity of polo-like kinase inhibitor volasertib (BI6727) in vitro and in vivo was determined.
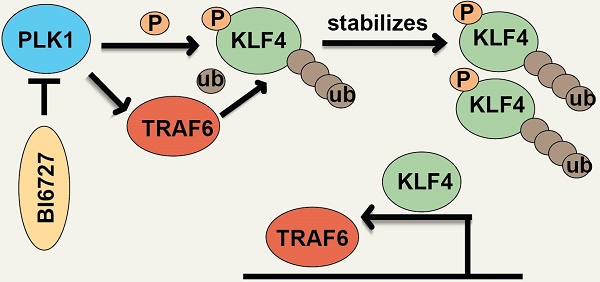
Result: Our investigation showed that high expression of KLF4 was correlated with poor prognosis in NPC. Moreover, genome-wide profiling revealed that KLF4 directly activated oncogenic programmes, including gene sets associated with KRAS, VEGF, and MYC signalling. We further found that inhibition of polo-like kinase 1 could downregulate the expression of KLF4 and that PLK1 directly phosphorylated KLF4 at Ser234. Notably, phosphorylation of KLF4 by PLK1 caused the recruitment and binding of the E3 ligase TRAF6, which resulted in KLF4 K32 K63-linked ubiquitination and stabilization. Moreover, KLF4 could enhance TRAF6 expression at the transcriptional level, thus initiating a KLF4-TRAF6 feed-forward loop. Treatment with the PLK1 inhibitor volasertib (BI6727) significantly inhibited tumor growth in nude mice.
Conclusion: Our study unveiled a new PLK1-TRAF6-KLF4 feed-forward loop. The resulting increase in KLF4 ubiquitination leads to stabilization and upregulation of KLF4, which leads to tumorigenesis in NPC. These results expand our understanding of the role of KLF4 in NPC and validate PLK1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for NPC, especially cancer patients with KLF4 overexpression.
Keywords: PLK1, KLF4, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, K63-linked ubiquitination
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact