13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(19):5497-5516. doi:10.7150/thno.33800 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The miR-26a/AP-2α/Nanog signaling axis mediates stem cell self-renewal and temozolomide resistance in glioma
1. State Key Laboratory of Developmental Biology of Freshwater Fish, College of Life Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410081, China;
2. Key Laboratory of Protein Chemistry and Development Biology of State Education Ministry of China, College of Life Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, Hunan, 410081, China;
3. The National & Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Animal Peptide Drug Development, College of Life Science, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, 410081, China;
4. Department of Neurosurgery, Hunan Provincial Tumor Hospital, The Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Xiangya Medical School of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410013, China;
5. Aier School of Ophthalmology, Central South University; Aier Eye Institute, Changsha, Hunan, 410015, China;
6. Department of Endocrinology, Endocrinology Research Center, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China;
7. College of Engineering and Design, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, Human, 410081, China;
8. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of New Mexico Health Sciences Center, Albuquerque, NM, 87131, USA;
9. Department of Neurosurgery, Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, Hunan, 410008, China.
* These authors equally contributed to this work.
Abstract
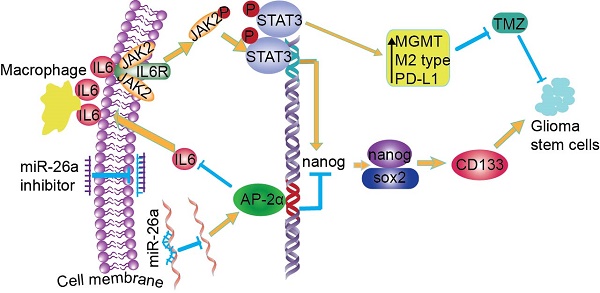
Aberrant expression of transcription factor AP-2α has been functionally associated with various cancers, but its clinical significance and molecular mechanisms in human glioma are largely elusive.
Methods: AP-2α expression was analyzed in human glioma tissues by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in glioma cell lines by Western blot. The effects of AP-2α on glioma cell proliferation, migration, invasion and tumor formation were evaluated by the 3-(4,5-dimethyNCthiazol-2-yl)-25-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and transwell assays in vitro and in nude mouse models in vivo. The influence of AP-2α on glioma cell stemness was analyzed by sphere-formation, self-renewal and limiting dilution assays in vitro and in intracranial mouse models in vivo. The effects of AP-2α on temozolomide (TMZ) resistance were detected by the MTT assay, cell apoptosis, real-time PCR analysis, western blotting and mouse experiments. The correlation between AP-2α expression and the expression of miR-26a, Nanog was determined by luciferase reporter assays, electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and expression analysis.
Results: AP-2α expression was downregulated in 58.5% of glioma tissues and in 4 glioma cell lines. AP-2α overexpression not only reduced the proliferation, migration and invasion of glioma cell lines but also suppressed the sphere-formation and self-renewal abilities of glioma stem cells in vitro. Moreover, AP-2α overexpression inhibited subcutaneous and intracranial xenograft tumor growth in vivo. Furthermore, AP-2α enhanced the sensitivity of glioma cells to TMZ. Finally, AP-2α directly bound to the regulatory region of the Nanog gene, reduced Nanog, Sox2 and CD133 expression. Meanwhile, AP-2α indirectly downregulated Nanog expression by inhibiting the interleukin 6/janus kinase 2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (IL6/JAK2/STAT3) signaling pathway, consequently decreasing O6-methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) and programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. In addition, miR-26a decreased AP-2α expression by binding to the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of AP-2α and reversed the tumor suppressive role of AP-2α in glioma, which was rescued by a miR-26a inhibitor. TMZ and the miR-26a inhibitor synergistically suppressed intracranial GSC growth.
Conclusion: These results suggest that AP-2α reduces the stemness and TMZ resistance of glioma by inhibiting the Nanog/Sox2/CD133 axis and IL6/STAT3 signaling pathways. Therefore, AP-2α and miR-26a inhibition might represent a new target for developing new therapeutic strategies in TMZ resistance and recurrent glioma patients.
Keywords: AP-2α, glioma, glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs), TMZ resistance, Nanog, STAT3, miR-26a
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact