13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(19):5558-5576. doi:10.7150/thno.34463 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Long noncoding RNA GAS5 induces abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by promoting smooth muscle apoptosis
1. Department of Cardiology, State Key Laboratory of Organ Failure Research, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
2. Department of Oncology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China
*These authors contributed equally to this work
Abstract
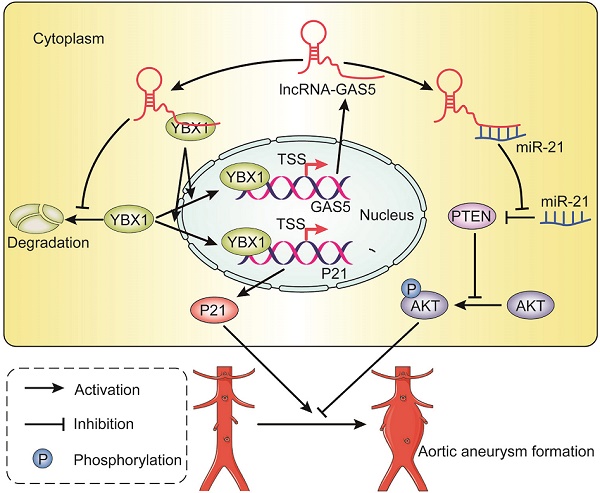
Objective: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) may serve as specific targets for the treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs). LncRNA GAS5, functionally associated with smooth muscle cell (SMC) apoptosis and proliferation, is likely involved in AAA formation, but the exact role of GAS5 in AAA is unknown. We thus explored the contribution of GAS5 to SMC-regulated AAA formation and its underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Human specimens were used to verify the diverse expression of GAS5 in normal and AAA tissues. The angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced AAA model in ApoE-/- mice and the CaCl2-induced AAA model in wild-type C57BL/6 mice were used. RNA pull-down and luciferase reporter gene assays were performed in human aortic SMCs to detect the interaction between GAS5 and its downstream targets of protein or microRNA (miR).
Results: GAS5 expression was significantly upregulated in human AAA specimens and two murine AAA models compared to human normal aortas and murine sham-operated controls. GAS5 overexpression induced SMC apoptosis and repressed its proliferation, thereby promoting AAA formation in two murine AAA models. Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) was identified as a direct target of GAS5 while it also formed a positive feedback loop with GAS5 to regulate the downstream target p21. Furthermore, GAS5 acted as a miR-21 sponge to release phosphatase and tensin homolog from repression, which blocked the activation and phosphorylation of Akt to inhibit proliferation and promote apoptosis in SMCs.
Conclusion: The LncRNA GAS5 contributes to SMC survival during AAA formation. Thus, GAS5 might serve as a novel target against AAA.
Keywords: GAS5, abdominal aortic aneurysm, Y-box-binding protein 1, microRNA-21, smooth muscle cell apoptosis
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact