13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(22):6532-6549. doi:10.7150/thno.35057 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A stage-specific cancer chemotherapy strategy through flexible combination of reduction-activated charge-conversional core-shell nanoparticles
1. Department of Pharmaceutical Analysis, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
2. Department of Natural Medicinal Chemistry, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing 210009, China
3. The Joint Laboratory of Chinese Pharmaceutical University and Taian City Central Hospital, Taian City Central Hospital, Taian, 271000, China
4. Taian City institute of Digestive Disease, Taian City Central Hospital, Taian, 271000, China
5. Pharmaceutical Department, Taian City Central Hospital, Taian, 271000, China
6. Jiangsu Food and Pharmaceutical Science College, Huaian 223003, China
7. Hangzhou Institute of Pharmaceutical Innovation, China Pharmaceutical University, Hangzhou 310018, China
Abstract
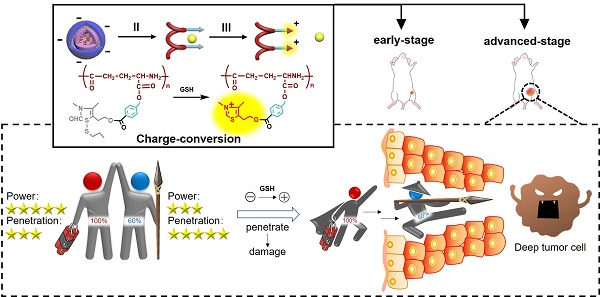
Precision medicine has increased the demand for stage-specific cancer chemotherapy. Drugs with different properties are needed for different stages of tumor development, which is, inducing rapid destruction in the early stage and facilitating deep penetration in the advanced stage. Herein, we report a novel reduction-activated charge-conversional core-shell nanoparticle (CS NP) formula based on ring-closing metathesis of the thiamine disulfide system (TDS) to deliver the chemotherapeutic agent-gambogic acid (GA).
Methods: The shell consisted of hyaluronic acid-all-trans retinoid acid with a disulfide bond as the linker (HA-SS-ATRA). The core was selected from poly (γ-glutamic acid) with different grafting rates of the functional group (Fx%) of TDS. GA/CF100%S NPs, with the strongest reduction-responsive drug release, and GA/CF60%S NPs with the strongest penetration have been finally screened. On this basis, a stage-specific administration strategy against a two-stage hepatocellular carcinoma was proposed.
Results: The developed CS NPs have been confirmed as inducing reduction-activated charge conversion from about -25 to +30 mV with up to 95% drug release within 48 h. The administration strategy, GA/CF100%S NPs for the early-stage tumor, and sequential administration of GA/CF60%S NPs followed by GA/CF100%S NPs for the advanced-stage tumor, achieved excellent tumor inhibition rates of 93.86±2.94% and 90.76±6.43%, respectively.
Conclusions: Our CS NPs provide a novel platform for charge conversion activated by reduction. The stage-specific administration strategy showed great promise for cancer therapy.
Keywords: charge conversion, reduction-activated, tumor penetration, stage-specific chemotherapy, hepatocellular carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact