13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(23):6991-7002. doi:10.7150/thno.35791 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Anti-edema and antioxidant combination therapy for ischemic stroke via glyburide-loaded betulinic acid nanoparticles
1. Department of Neurosurgery, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 06510, USA.
2. Department of Neurosurgery, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan 430060, China.
3. College of Biological Sciences and Biotechnology, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing 100083, China.
4. School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150090, China.
5. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 06510, USA
6. PET Center, Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 06510, USA
7. Department of Neurology, Division of Neurocritical Care, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, 02114, USA.
8. Department of Neurosurgery, University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, 21201, USA.
9. Department of Neurology, Yale University, New Haven, CT, 06510, USA.
*These authors contributed equally.
Abstract
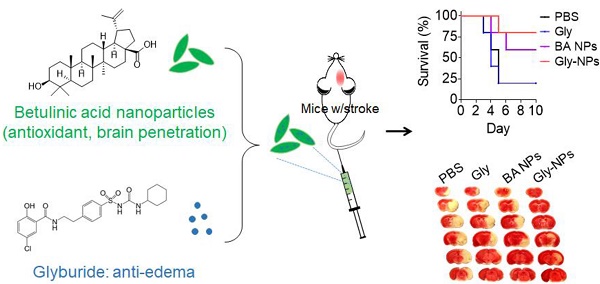
Stroke is a deadly disease without effective pharmacotherapies, which is due to two major reasons. First, most therapeutics cannot efficiently penetrate the brain. Second, single agent pharmacotherapy may be insufficient and effective treatment of stroke requires targeting multiple complementary targets. Here, we set to develop single component, multifunctional nanoparticles (NPs) for targeted delivery of glyburide to the brain for stroke treatment.
Methods: To characterize the brain penetrability, we radiolabeled glyburide, intravenously administered it to stroke- bearing mice, and determined its accumulation in the brain using positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET/CT). To identify functional nanomaterials to improve drug delivery to the brain, we developed a chemical extraction approach and tested it for isolation of nanomaterials from E. ulmoides, a medicinal herb. To assess the therapeutic benefits, we synthesized glyburide-loaded NPs and evaluated them in stroke- bearing mice.
Results: We found that glyburide has a limited ability to penetrate the ischemic brain. We identified betulinic acid (BA) capable of forming NPs, which, after intravenous administration, efficiently penetrate the brain and significantly reduce ischemia-induced infarction as an antioxidant agent. We demonstrated that BA NPs enhance delivery of glyburide, leading to therapeutic benefits significantly greater than those achieved by either glyburide or BA NPs.
Conclusion: This study suggests a new direction to identify functional nanomaterials and a simple approach to achieving anti-edema and antioxidant combination therapy. The resulting glyburide- loaded BA NPs may be translated into clinical applications to improve clinical management of stroke.
Keywords: ischemic stroke, betulinic acid, glyburide, antioxidant, combination therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact