13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2019; 9(26):8266-8276. doi:10.7150/thno.36986 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Renal Clearable Ru-based Coordination Polymer Nanodots for Photoacoustic Imaging Guided Cancer Therapy
Institute of Functional Nano & Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China.
Abstract
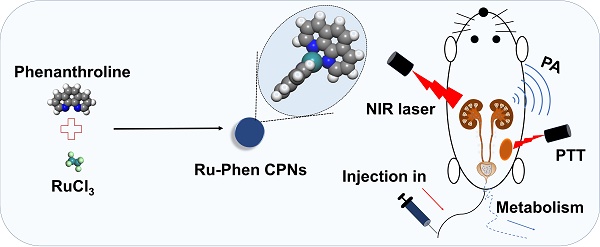
Rationale: Despite the promises of applying theranostic nanoagents for imaging-guided cancer therapy, the chronic retention of these nanoagents may cause safety concerns that hinder their future clinical applications. The metabolizable nanoagents with rapid renal excretion to avoid long-term toxicity is a possible solution for this issue.
Method: Herein, we synthesize ultra-small metal-organic coordination polymer nanodots based on ruthenium ion (Ru3+) / phenanthroline (Phen) (Ru-Phen CPNs) with superior near-infrared (NIR) absorption. The size, photothermal conversion, cytotoxicity, photoacoustic imaging, in vivo & in vitro cancer treatment efficiency and biosafety are tested.
Results: The size of the ultra-small Ru-Phen CPNs is 6.5 nm. The photothermal conversion efficiency is measured to be ~ 60.69 %, much higher than that of previously reported photothermal agents. The Ru-Phen CPNs could be employed for photoacoustic (PA, 808 nm) imaging-guided photothermal therapy (PTT, 808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2) with great performance. Notably, the intrinsic PA signals (808 nm) of Ru-Phen CPNs are observed in kidneys of treated mice, illustrating efficient renal clearance of those ultra-small CPNs. Moreover, the clearance of CPNs is further confirmed by detecting Ru levels in urine and feces.
Conclusion: Our work presents a new type of ultra-small Ru-based CPNs with a record high photothermal conversion efficiency, efficient tumor retention after systemic administration, and rapid renal excretion to avoid long-term toxicity, promising for imaging-guided photothermal therapy.
Keywords: Ru-Phen CPNs, ultra-small size nanodots, photoacoustic imaging, photothermal therapy, renal clearance
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact