13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(2):498-515. doi:10.7150/thno.37745 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting the STING pathway in tumor-associated macrophages regulates innate immune sensing of gastric cancer cells
1. State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China.
2. Department of Pediatric Surgery, Guangzhou Women and Children's Medical Center, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
3. Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China.
4. Department of Medical Oncology, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangzhou 510060, China.
5. Zhongshan School of Medicine, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510060, China.
* Contribute equally
Abstract
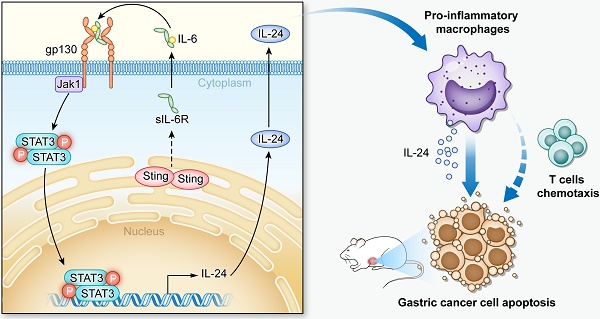
Rationale: STING is a critical player in the innate and adaptive immune system, sensing cytosolic DNA to activate the expression of interferon genes and regulate T lymphocytes, which drives immunogenic responses to cancer cells. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), abundantly present in the tumor microenvironment, play a key role in cancer development. Gastric cancer is one of the most common and leading causes in cancer-related death worldwide. However, studies on the function and regulation of STING in TAMs and their roles in gastric cancer progression are still limited.
Methods: We analyzed STING and CD68 expression of 200 pairs of gastric cancer and adjacent normal tissues by immunohistochemistry to identify the prognostic values of STING, as well as the correlations between STING and CD68 in gastric cancer. The characteristics of STING-altered macrophages, as well as their effects on cancer cell apoptosis and T cell differentiation were examined by flow cytometry. Cytokines secreted by STING-altered macrophages were identified by the Human Inflammation Array3 kit. Concentrations of soluble IL24 and IFN-β were measured by ELISA. In vivo models, including spontaneous gastric cancer in p53+/- mice and cell line-based xenografts, were established, and clinical benefits of STING-altered macrophages were examined.
Results: Our study identifies STING as a prognostic factor for gastric cancer, and for the first time demonstrated that knocking-down STING and STING activation by 2'3'-c-GAMP both promote TAMs polarizing into pro-inflammatory subtype and induce apoptosis of gastric cancer cells, mechanistically through IL6R-JAK-IL24 pathway.
Conclusions: This study evaluated effects of targeting STING in TAMs in anti-gastric-cancer therapies. Moreover, we unveil a novel function of STING to activate the IL6R-JAK-IL24 pathway in macrophages.
Keywords: Gastric carcinoma, STING, apoptosis, IL-24, IL-6R
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact