13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(2):757-781. doi:10.7150/thno.39701 This issue Cite
Review
Two-dimensional nanomaterials beyond graphene for antibacterial applications: current progress and future perspectives
1. CAS Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials and Nanosafety, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
2. CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China.
3. College of Materials Science and Optoelectronic Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
Abstract
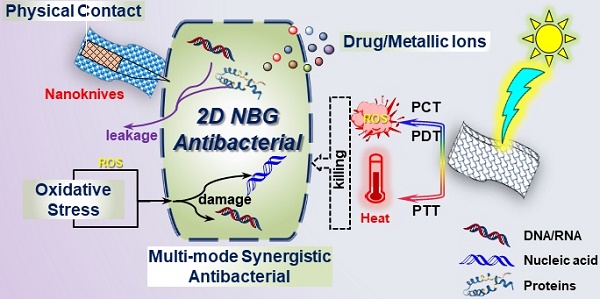
The marked augment of drug-resistance to traditional antibiotics underlines the crying need for novel replaceable antibacterials. Research advances have revealed the considerable sterilization potential of two-dimension graphene-based nanomaterials. Subsequently, two-dimensional nanomaterials beyond graphene (2D NBG) as novel antibacterials have also demonstrated their power for disinfection due to their unique physicochemical properties and good biocompatibility. Therefore, the exploration of antibacterial mechanisms of 2D NBG is vital to manipulate antibacterials for future applications. Herein, we summarize the recent research progress of 2D NBG-based antibacterial agents, starting with a detailed introduction of the relevant antibacterial mechanisms, including direct contact destruction, oxidative stress, photo-induced antibacterial, control drug/metallic ions releasing, and the multi-mode synergistic antibacterial. Then, the effect of the physicochemical properties of 2D NBG on their antibacterial activities is also discussed. Additionally, a summary of the different kinds of 2D NBG is given, such as transition-metal dichalcogenides/oxides, metal-based compounds, nitride-based nanomaterials, black phosphorus, transition metal carbides, and nitrides. Finally, we rationally analyze the current challenges and new perspectives for future study of more effective antibacterial agents. This review not only can help researchers grasp the current status of 2D NBG antibacterials, but also may catalyze breakthroughs in this fast-growing field.
Keywords: bacterial resistance, antibacterials, 2D NBG, antibacterial mechanisms, physicochemical properties
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact