13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(22):10120-10140. doi:10.7150/thno.49147 This issue Cite
Research Paper
A reciprocal feedback of Myc and lncRNA MTSS1-AS contributes to extracellular acidity-promoted metastasis of pancreatic cancer
1. Department of Emergency Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
2. Department of Gastroenterology Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
3. Department of Pancreatic Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this manuscript as co-first authors.
Abstract
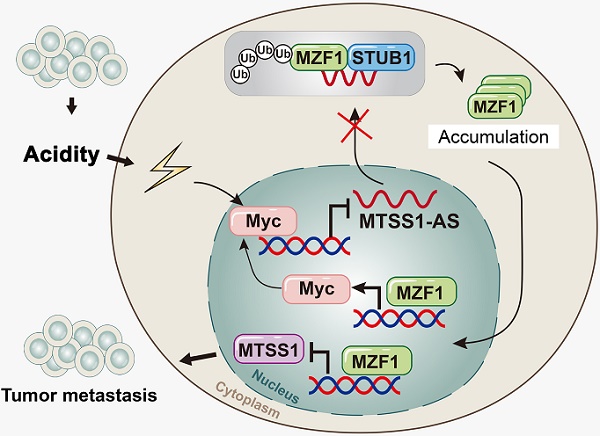
Rationale: Previous studies have reported on the role of extracellular acidity in the metastasis of numerous cancers. However, the involvement of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) in the extracellular acidity-induced cancer metastasis of pancreatic cancer (PC) remains unclear.
Methods: Different expression levels of lncRNAs in PC cells under normal and acidic conditions were compared by RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). The effects of antisense lncRNA of metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1-AS) on acidic PC cells were assessed by gain- and loss-of-function experiments. Fluorescence in situ hybridization, RNA immunoprecipitation, RNA pull-down, Western blot, luciferase reporter, and Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays were employed to determine the regulatory mechanisms of MTSS1-AS in the acidity-induced metastasis of PC cells. The expression of MTSS1-AS and associated pathways were compared in PC samples and peritumoral normal tissues.
Results: RNA-seq demonstrated that MTSS1-AS was significantly downregulated in pancreatic cells cultured with the acidic medium. The overexpression of MTSS1-AS remarkably inhibited the acidity-promoted metastasis of PC cells by upregulating the expression of its sense gene metastasis suppressor 1 (MTSS1). Mechanistically, MTSS1-AS scaffolded the interaction between E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase STIP1 homology and U-box containing protein 1 (STUB1) and transcription regulator myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1), leading to ubiquitination-mediated degradation of MZF1. Further, MZF1 inhibited the expression of MTSS1 by binding to the MTSS1 promoter. Thus, the acidity-reduced MTSS1-AS facilitated the stability of MZF1 and its inhibitory effect on MTSS1 transcription, thereby promoting the metastasis of PC cells under acidic conditions. Moreover, MTSS1-AS was transcriptionally repressed by the binding of MYC proto-oncogene (Myc) with initiator (Inr) elements of the MTSS1-AS promoter. Meanwhile, MTSS1-AS mutually repressed the expression of Myc by impairing the MZF1-mediated transcription activation of Myc, thereby forming a negative feedback loop between MTSS1-AS and Myc in acidic PC cells. In accordance with the experimental results, MTSS1-AS and MTSS1 were downregulated in PC and correlated with poor overall survival.
Conclusions: The results implicated that a reciprocal feedback loop between Myc and MTSS1-AS contributed to the extracellular acidity-promoted metastasis of PC, and indicated that MTSS1-AS was a valuable biomarker and therapeutic target for PC.
Keywords: Acidity, LncRNA, metastasis, MTSS1-AS, Myc
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact