13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10589-10605. doi:10.7150/thno.47176 This issue Cite
Research Paper
EREG-driven oncogenesis of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma exhibits higher sensitivity to Erlotinib therapy
1. Department of Oral and Maxillofacial-Head and Neck Oncology, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
2. Laboratory of Oral Microbiota and Systemic Diseases, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, College of Stomatology, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
3. National Clinical Research Center for Oral Diseases, Shanghai Key Laboratory of Stomatology & Shanghai Research Institute of Stomatology, Shanghai, China.
4. Department of Molecular and Cellular Oncology, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, 77030, USA.
*Shuli Liu, Yang Wang and Yong Han equally contributed to this work
Abstract
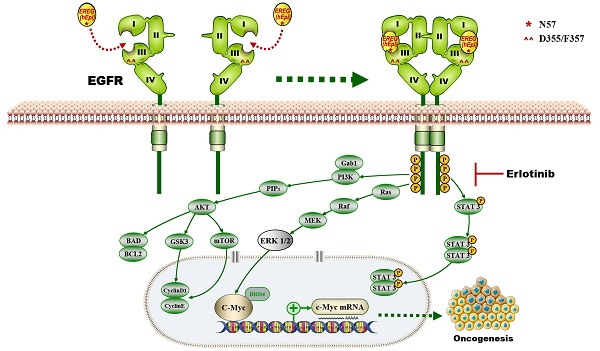
Rationale: The oncogenesis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is believed to result from oncogene activation and tumor suppressor inactivation. Here, we identified a new oncogenic role for the EREG gene in HNSCC.
Methods: The TCGA database and immunohistochemistry assay were used to analyze expression of EREG in HNSCC tissues. Immunoblotting was performed to identify the EGFR-mediated pathways altered by EREG. The role of EREG in oncogenesis was investigated in vivo and in vitro.
Results: Upregulated EREG expression predicted a poor prognosis and triggered HNSCC oncogenic transformation by activating the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling pathway. We also demonstrated the direct association of EREG with EGFR and that this binding required EGFR domains I and III and the N57 residue of EREG. Moreover, EREG overexpression was shown to promote HNSCC oncogenesis by inducing C-Myc expression, and the pharmacological inhibition of C-Myc rescued EREG-promoted HNSCC oncogenesis. Unlike other EGFR ligands, EREG could mimic EGFR mutations by sustaining the activation of the EGFR-Erk pathway, and high EREG expression was positively associated with the response to treatment with the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib. Furthermore, knockdown of EREG decreased sensitivity to erlotinib treatment in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: These results identify the EREG-EGFR-C-Myc pathway as a crucial axis that drives HNSCC oncogenesis and show that EREG expression could be a predictive functional marker of sensitivity to erlotinib therapy in HNSCC.
Keywords: Epiregulin, HNSCC, EGFR, C-Myc, Erlotinib
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact