13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10729-10742. doi:10.7150/thno.46297 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The ERα-miR-575-p27 feedback loop regulates tamoxifen sensitivity in ER-positive Breast Cancer
1. The First Department of Breast Cancer, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin 300060, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin 300060, China.
3. Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin 300060, China.
4. Key Laboratory of Breast Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin Medical University, Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300060, China.
5. Department of Surgical Oncology, Provincial Clinical College, Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou 350001, China.
6. Department of Anesthesiology, Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin 300060, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
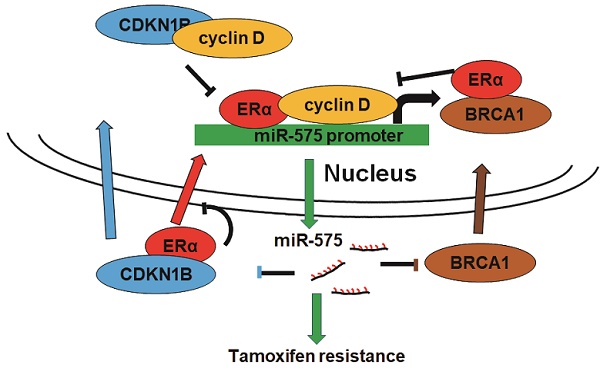
Background: Breast cancer is the most common malignancy, and approximately 70% of breast cancers are estrogen receptor-α (ERα) positive. The anti-estrogen tamoxifen is a highly effective and commonly used treatment for patients with ER+ breast cancer. However, 30% of breast cancer patients fail adjuvant tamoxifen therapy and most of metastatic breast cancer patients develop tamoxifen resistance. Although increasing evidence suggests that microRNA (miRNA) dysregulation influences tamoxifen sensitivity, the mechanism of the cross-talk between miRNA and ERα signaling remains unclear. miR-575 has been reported to be involved in carcinogenesis and progression, however, the role of miR-575 in breast cancer remains limited. The aim of this study was to understand the mechanism of miR-575 in breast cancer tamoxifen resistance.
Method: RT-qPCR was employed to assess miR-575 expression in breast cancer tissues and cell lines. The association of miR-575 expression with overall survival in patients with breast cancer was evaluated with KM plotter. Additionally, the effects of miR-575 on breast cancer proliferation and tamoxifen sensitivity were investigated both in vitro and in vivo. Bioinformatic analyses and luciferase reporter assays were performed to validate CDKN1B and BRCA1 as direct targets of miR-31-5p. The ERα binding sites in the miR-575 promoter region was validated with ChIP and luciferase assays. ERα interactions with CDKN1B, cyclin D1 or BRCA1 were determined by IP analysis, and protein expression levels and localization were analyzed by western blotting and immunofluorescence, respectively.
Results: miR-575 levels were higher in ER+ breast cancer than in ER- breast cancer and patients with high miR-575 expression had a significantly poorer outcome than those with low miR-575 expression. ERα bound the miR-575 promoter to activate its transcription, and tamoxifen treatment downregulated miR-575 expression in ER+ breast cancer. Overexpression of miR-575 decreased tamoxifen sensitivity by targeting CDKN1B and BRCA1. CDKN1B and BRCA1 were both able to antagonize ERα activity by inhibiting ERα nuclear translocation and interaction with cyclin D1. Furthermore, miR-575 expression was found to be upregulated in ER+ breast cancer cell with acquired tamoxifen resistance, whereas depletion of miR-575 partially re-sensitized these cells to tamoxifen by regulation of CDKN1B.
Conclusions: Our data reveal the ERα-miR-575-CDKN1B feedback loop in ER+ breast cancer, suggesting that miR-575 can be used as a prognostic biomarker in patients with ER+ breast cancer, as well as a predictor or a promising target for tamoxifen sensitivity.
Keywords: miR-575 regulates ER+ breast cancer tamoxifen sensitivity
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact