13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(23):10838-10848. doi:10.7150/thno.50283 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Tumor immune profiles noninvasively estimated by FDG PET with deep learning correlate with immunotherapy response in lung adenocarcinoma
1. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
2. Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
3. Department of Nuclear Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
4. Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
5. Cancer Research Institute, Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
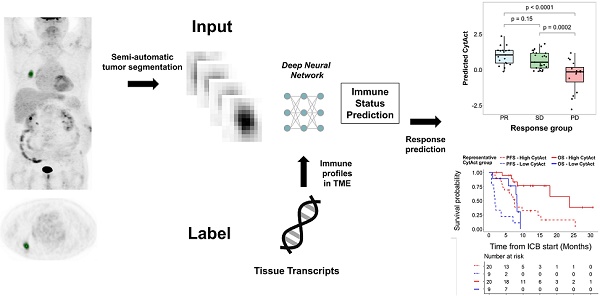
Rationale: The clinical application of biomarkers reflecting tumor immune microenvironment is hurdled by the invasiveness of obtaining tissues despite its importance in immunotherapy. We developed a deep learning-based biomarker which noninvasively estimates a tumor immune profile with fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD).
Methods: A deep learning model to predict cytolytic activity score (CytAct) using semi-automatically segmented tumors on FDG-PET trained by a publicly available dataset paired with tissue RNA sequencing (n = 93). This model was validated in two independent cohorts of LUAD: SNUH (n = 43) and The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) cohort (n = 16). The model was applied to the immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) cohort, which consists of patients with metastatic LUAD who underwent ICB treatment (n = 29).
Results: The predicted CytAct showed a positive correlation with CytAct of RNA sequencing in validation cohorts (Spearman rho = 0.32, p = 0.04 in SNUH cohort; spearman rho = 0.47, p = 0.07 in TCGA cohort). In ICB cohort, the higher predicted CytAct of individual lesion was associated with more decrement in tumor size after ICB treatment (Spearman rho = -0.54, p < 0.001). Higher minimum predicted CytAct in each patient associated with significantly prolonged progression free survival and overall survival (Hazard ratio 0.25, p = 0.001 and 0.18, p = 0.004, respectively). In patients with multiple lesions, ICB responders had significantly lower variance of predicted CytActs (p = 0.005).
Conclusion: The deep learning model that predicts CytAct using FDG-PET of LUAD was validated in independent cohorts. Our approach may be used to noninvasively assess an immune profile and predict outcomes of LUAD patients treated with ICB.
Keywords: Immunotherapy, tumor microenvironment, fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography, deep learning, gene expression profile
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact