13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(3):1107-1121. doi:10.7150/thno.38346 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The combination of bevacizumab/Avastin and erlotinib/Tarceva is relevant for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the role of a synonymous mutation of the EGFR receptor
1. Centre Scientifique de Monaco, Biomedical Department, 8 Quai Antoine Ier, MC-98000 Monaco, Principality of Monaco.
2. University Cote d'Azur, Institute for research on cancer and aging of Nice (IRCAN) CNRS UMR 7284/ INSERM U 1081 3
3. Department of Pathology, Nice University Hospital, University of Nice Sophia Antipolis.
4. Centre Hospitalier Princesse Grace, Pathology department, Monaco.
5. Centre Hospitalier Princesse Grace, Urology department, Monaco.
Abstract
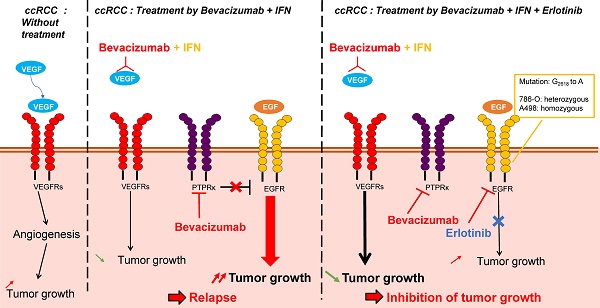
Metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinomas (mRCC) over-express the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Hence, the anti-VEGF antibody bevacizumab/Avastin (BVZ) combined with interferon alpha (IFN) was approved for the treatment of mRCC. However, approval was lost in July 2016 due to the absence of sustained efficacy. We previously showed that BVZ accelerates tumor growth in experimental models of mRCC in mice, results in part explained by down-regulation of the phospho tyrosine phosphatase receptor kappa (PTPRκ) in tumor cells. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a direct target of PTPRκ. Its down-regulation leads to constitutive activation of EGFR, an observation which prompted us to test the effect of the EGFR inhibitor erlotinib/Tarceva (ERLO) in addition to BVZ/IFN. The influence of the long non-coding RNA, EGFR-AS1, on ERLO efficacy was also addressed.
Methods: The effect of BVZ/IFN/ERLO was tested on the growth of experimental tumors in nude mice. The presence of germline mutation in the EGFR was evaluated on cell lines and primary RCC cells. In vitro translation and transfections of expression vectors coding the wild-type or the EGFR mutated gene in HEK-293 cells were used to test the role of EGFR mutation of the ERLO efficacy. Correlation between EGFR/EGFR-AS1 expression and survival was analyzed with an online available data base (TCGA).
Results: Tumor growth was strongly reduced by the triple combination BVZ/IFN/ERLO and linked to reduced levels of pro-angiogenic/pro-inflammatory cytokines of the ELR+CXCL family and to subsequent inhibition of vascularization, a decreased number of lymphatic vessels and polarization of macrophages towards the M1 phenotype. Cells isolated from surgical resection of human tumors presented a range of sensitivity to ERLO depending on the presence of a newly detected mutation in the EGFR and to the presence of EGFR-AS1.
Conclusions: Our results point-out that the BVZ/IFN/ERLO combination deserves testing for the treatment of mRCC that have a specific mutation in the EGFR.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact