13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(24):11264-11277. doi:10.7150/thno.47039 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Comprehensive characterization of functional eRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma reveals novel regulators and a prognosis-related molecular subtype
1. Department of Epidemiology, Center for Global Health, School of Public Health, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China.
2. Jiangsu Key Lab of Cancer Biomarkers, Prevention and Treatment, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211166, China.
3. Department of Bioinformatics, School of Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 211116, China.
4. Department of Thoracic Surgery, Jiangsu Cancer Hospital, Jiangsu Institute of Cancer Research, Nanjing Medical University Affiliated Cancer Hospital, Nanjing 210029, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
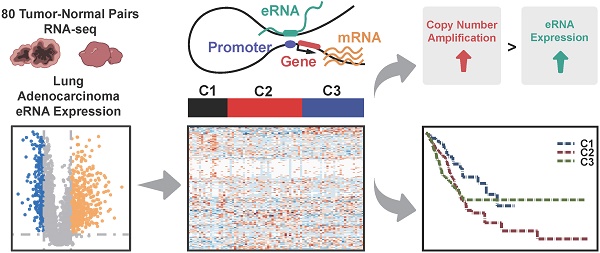
Rationale: As the transcriptional products of active enhancers, enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) are essential for the initiation of tumorigenesis. However, the landscape and functional characteristics of eRNAs in Chinese lung adenocarcinoma, and the clinical utility of eRNA-based molecular subtypes remain largely unknown.
Methods: A genome-wide profiling of eRNAs was performed in 80 Chinese lung adenocarcinoma patients with RNA-seq data. Functional eRNAs and associated genes were identified between paired adenocarcinoma and adjacent samples. Unsupervised clustering of functional eRNAs was conducted and the associations with molecular characteristics and clinical outcomes were accessed by integrating whole-genome sequencing data and clinical data. Additionally, 481 lung adenocarcinoma patients were used for the validation based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset.
Results: A total of 3297 eRNAs with sufficient expression were identified, which were globally upregulated in adenocarcinoma samples compared to matched-adjacent pairs (P = 7.61×10-3). Further analyses indicated that these upregulated eRNAs were correlated with copy number amplification (CNA) status (Cor = 0.22, P = 0.045), and eRNA-correlated genes were primarily involved in cell cycle and immune system-related pathways. Based on the co-expression analysis of eRNAs with protein-coding genes, we defined 188 functional eRNAs and their correlated genes were overrepresented in cancer driver genes (ER = 1.98, P = 5.95×10-12) and clinically-actionable genes (ER = 2.19, P = 3.44×10-4). The eRNA-based consensus clustering further identified a novel molecular subtype with immune deficiency and a high-level of genomic alterations, which was associated with poor clinical outcomes of lung adenocarcinoma patients (OS: HR = 1.91, P = 0.015; PFI: HR = 1.64, P = 0.034).
Conclusions: The genome-wide identification and characterization of eRNAs reveal novel regulators for the development of lung cancer, which provides a new biological dimension for the understanding of eRNAs during lung carcinogenesis and emphasize the clinical utility of eRNA-based molecular subtypes in the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma, enhancer RNA, immune deficiency, prognosis, copy number amplification
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact