13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(25):11428-11443. doi:10.7150/thno.47432 This issue Cite
Research Paper
BET inhibitor suppresses melanoma progression via the noncanonical NF-κB/SPP1 pathway
1. Department of Dermatology, Hunan Engineering Research Center of Skin Health and Disease, Hunan Key Laboratory of Skin Cancer and Psoriasis, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
2. National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, Hunan 410008, China.
3. Department of PET Center, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, 410008, China.
*Guangtong Deng and Furong Zeng contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
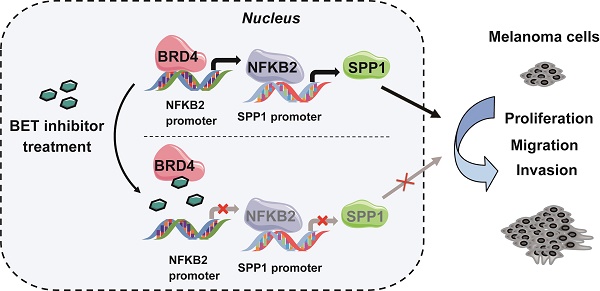
Background: Bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) inhibitors have shown profound efficacy against hematologic malignancies and solid tumors in preclinical studies. However, the underlying molecular mechanism in melanoma is not well understood. Here we identified secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1) as a melanoma driver and a crucial target of BET inhibitors in melanoma. Methods: Bioinformatics analysis and meta-analysis were used to evaluate the SPP1 expression in normal tissues, primary melanoma, and metastatic melanoma. Real-time PCR (RT-PCR) and Western blotting were employed to quantify SPP1 expression in melanoma cells and tissues. Cell proliferation, wound healing, and Transwell assays were carried out to evaluate the effects of SPP1 and BET inhibitors in melanoma cells in vitro. A xenograft mouse model was used to investigate the effect of SPP1 and BET inhibitors on melanoma in vivo. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was performed to evaluate the regulatory mechanism of BET inhibitors on SPP1. Results: SPP1 was identified as a melanoma driver by bioinformatics analysis, and meta-analysis determined it to be a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for melanoma. SPP1 overexpression was associated with poor melanoma prognosis, and silencing SPP1 suppressed melanoma cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Through a pilot drug screen, we identified BET inhibitors as ideal therapeutic agents that suppressed SPP1 expression. Also, SPP1 overexpression could partially reverse the suppressive effect of BET inhibitors on melanoma. We further demonstrated that bromodomain-containing 4 (BRD4) regulated SPP1 expression. Notably, BRD4 did not bind directly to the SPP1 promoter but regulated SPP1 expression through NFKB2. Silencing of NFKB2 resembled the phenotype of BET inhibitors treatment and SPP1 silencing in melanoma. Conclusion: Our findings highlight SPP1 as an essential target of BET inhibitors and provide a novel mechanism by which BET inhibitors suppress melanoma progression via the noncanonical NF-κB/SPP1 pathway.
Keywords: BET inhibitor, SPP1, noncanonical NF-κB pathway, melanoma.
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact