13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(26):11908-11920. doi:10.7150/thno.50616 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Graphene oxide improves postoperative cognitive dysfunction by maximally alleviating amyloid beta burden in mice
1. Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Key Laboratory of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine of Anhui Higher Education Institutes, Anhui Medical University.
2. Reproductive Medicine Center, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University; NHC Key Laboratory of Study on Abnormal Gametes and Reproductive Tract (Anhui Medical University); Key Laboratory of Population Health Across Life Cycle (Anhui Medical University), Ministry of Education of the People's Republic of China.
3. The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC, Division of Life Sciences and Medicine, University of Science and Technology of China.
4. School of Life Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China.
5. Nanobio Laboratory, Institute of Life Sciences, South China University of Technology.
#These authors contributed equally to the study.
Abstract
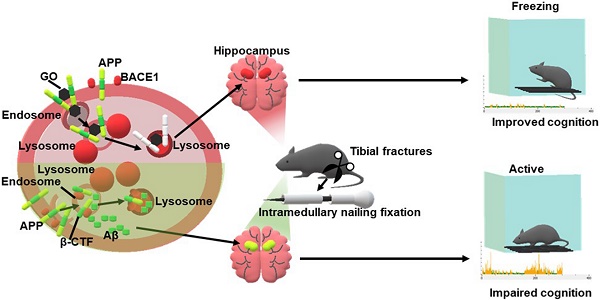
Rationale: Graphene oxide (GO) based nanomaterials have shown potential for the diagnosis and treatment of amyloid-β (Aβ)-related diseases, mainly on Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, these nanomaterials have limitations. How GO is beneficial to eliminate Aβ burden, and its physiological function in Aβ-related diseases, still needs to be investigated. Moreover, postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) is an Aβ-related common central nervous system complication, however, nanomedicine treatment is lacking.
Methods: To evaluate the effects of GO on Aβ levels, HEK293T-APP-GFP and SHSY5Y-APP-GFP cells are established. Intramedullary fixation surgery for tibial fractures under inhalation anesthesia is used to induce dysfunction of fear memory in mice. The fear memory of mice is assessed by fear conditioning test.
Results: GO treatment maximally alleviated Aβ levels by simultaneously reducing Aβ generation and enhancing its degradation through inhibiting β-cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) and improving endosomal Aβ delivery to lysosomes, respectively. In postoperative mice, the hippocampal Aβ levels were significantly increased and hippocampal-dependent fear memory was impaired. However, GO administration significantly reduced hippocampal Aβ levels and improved the cognitive function of the postoperative mice.
Conclusion: GO improves fear memory of postoperative mice by maximally alleviating Aβ accumulation, providing new evidence for the application of GO-based nanomedicines in Aβ-related diseases.
Keywords: graphene oxide, β-amyloid, postoperative cognitive dysfunction, fear memory
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact