13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(26):11921-11937. doi:10.7150/thno.46006 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Targeting Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1-mediated high oxidative stress suppresses EBV lytic reactivation and sensitizes tumors to radiation therapy
1. Key Laboratory of Cancer Carcinogenesis and Invasion, Chinese Ministry of Education, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China.
2. Cancer Research Institute and School of Basic Medicine Science, Xiangya School of Medicine, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China.
3. Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis, Chinese Ministry of Health, Changsha 410078, China.
4. Molecular Imaging Research Center of Central South University, Changsha 410078, China.
5. Research Center for Technologies of Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostics and Therapeutics, Changsha 410078, China.
6. National Joint Engineering Research Center for Genetic Diagnostics of Infectious Diseases and Cancer, Changsha 410078, China.
7. State Key Laboratory of Oncology in South China, Collaborative Innovation Center for Cancer Medicine, Guangdong Key Laboratory of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis and Therapy, Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center, Guangzhou, 510060, China.
8. Key Laboratory of Cancer Carcinogenesis and Invasion, Chinese Ministry of Education, Zhongshan Hospital, Shanghai Medical School, Fudan University, Shanghai 200000, China.
9. Department of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China.
10. Department of Radiology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China.
11. The Hormel Institute, University of Minnesota, Austin, MN 55912, USA.
Abstract
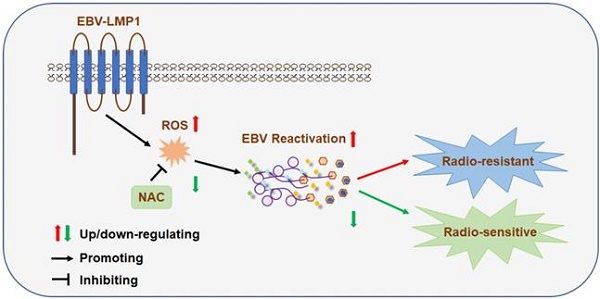
Generating oxidative stress is a critical mechanism by which host cells defend against infection by pathogenic microorganisms. Radiation resistance is a critical problem in radiotherapy against cancer. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a cancer-causing virus and its reactivation plays an important role in the development of EBV-related tumors. This study aimed to explore the inner relationship and regulatory mechanism among oxidative stress, EBV reactivation, and radioresistance and to identify new molecular subtyping models and treatment strategies to improve the therapeutic effects of radiotherapy.
Methods: ROS, NADP+/NADPH, and GSSG/GSH were detected to evaluate the oxidative stress of cells. 8-OHdG is a reliable oxidative stress marker to evaluate the oxidative stress in patients. Its concentration in serum was detected using an ELISA method and in biopsies was detected using IHC. qPCR array was performed to evaluate the expression of essential oxidative stress genes. qPCR, Western blot, and IHC were used to measure the level of EBV reactivation in vitro and in vivo. A Rta-IgG ELISA kit and EBV DNA detection kit were used to analyze the reactivation of EBV in serum from NPC patients. NPC tumor tissue microarrays was used to investigate the prognostic role of oxidative stress and EBV reactivation. Radiation resistance was evaluated by a colony formation assay. Xenografts were treated with NAC, radiation, or a combination of NAC and radiation. EBV DNA load of tumor tissue was evaluated using an EBV DNA detection kit. Oxidative stress, EBV reactivation, and the apoptosis rate in tumor tissues were detected by using 8-OHdG, EAD, and TUNEL assays, respectively.
Results: We found that EBV can induce high oxidative stress, which promotes its reactivation and thus leads to radioresistance. Basically, EBV caused NPC cells to undergo a process of 'Redox Resetting' to acquire a new redox status with higher levels of ROS accumulation and stronger antioxidant systems by increasing the expression of the ROS-producing enzyme, NOX2, and the cellular master antioxidant regulator, Nrf2. Also, EBV encoded driving protein LMP1 promotes EBV reactivation through production of ROS. Furthermore, high oxidative stress and EBV reactivation were positively associated with poor overall survival of patients following radiation therapy and were significant related to NPC patients' recurrence and clinical stage. By decreasing oxidative stress using an FDA approved antioxidant drug, NAC, sensitivity of tumors to radiation was increased. Additionally, 8-OHdG and EBV DNA could be dual prognostic markers for NPC patients.
Conclusions: Oxidative stress mediates EBV reactivation and leads to radioresistance. Targeting oxidative stress can provide therapeutic benefits to cancer patients with radiation resistance. Clinically, we, for the first time, generated a molecular subtyping model for NPC relying on 8-OHdG and EBV DNA level. These dual markers could identify patients who are at a high risk of poor outcomes but who might benefit from the sequential therapy of reactive oxygen blockade followed by radiation therapy, which provides novel perspectives for the precise treatment of NPC.
Keywords: oxidative stress, Epstein-Barr virus reactivation, radioresistance, prognostic bio-model, nasopharyngeal carcinoma
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact