13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(3):1230-1244. doi:10.7150/thno.38711 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The Roles of GSK-3β in Regulation of Retinoid Signaling and Sorafenib Treatment Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
1. State Key Laboratory of Cellular Stress Biology and Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Innovative Drug Target Research, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Xiamen University, Xiang'an, Xiamen 361102, China
2. The 174 th Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiang'an, Xiamen 361102, China
3. School of Biological Sciences, University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong
Abstract
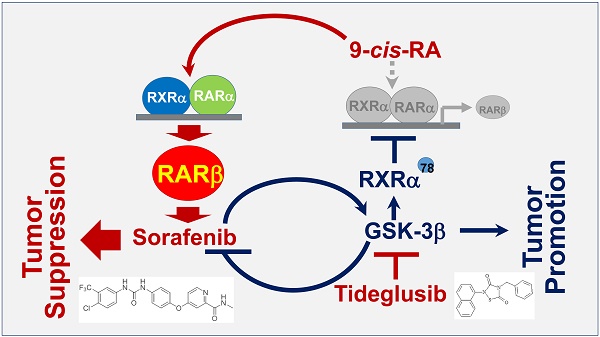
Rationale: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) plays key roles in metabolism and many cellular processes. It was recently demonstrated that overexpression of GSK-3β can confer tumor growth. However, the expression and function of GSK-3β in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain largely unexplored. This study is aimed at investigating the role and therapeutic target value of GSK-3β in HCC.
Methods: We firstly clarified the expression of GSK-3β in human HCC samples. Given that deviated retinoid signalling is critical for HCC development, we studied whether GSK-3β could be involved in the regulation. Since sorafenib is currently used to treat HCC, the involvement of GSK-3β in sorafenib treatment response was determined. Co-immunoprecipitation, GST pull down, in vitro kinase assay, luciferase reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation were used to explore the molecular mechanism. The biological readouts were examined with MTT, flow cytometry and animal experiments.
Results: We demonstrated that GSK-3β is highly expressed in HCC and associated with shorter overall survival (OS). Overexpression of GSK-3β confers HCC cell colony formation and xenograft tumor growth. Tumor-associated GSK-3β is correlated with reduced expression of retinoic acid receptor-β (RARβ), which is caused by GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation and heterodimerization abrogation of retinoid X receptor (RXRα) with RARα on RARβ promoter. Overexpression of functional GSK-3β impairs retinoid response and represses sorafenib anti-HCC effect. Inactivation of GSK-3β by tideglusib can potentiate 9-cis-RA enhancement of sorafenib sensitivity (tumor inhibition from 48.3% to 93.4%). Efficient induction of RARβ by tideglusib/9-cis-RA is required for enhanced therapeutic outcome of sorafenib, which effect is greatly inhibited by knocking down RARβ.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that GSK-3β is a disruptor of retinoid signalling and a new resistant factor of sorafenib in HCC. Targeting GSK-3β may be a promising strategy for HCC treatment in clinic.
Keywords: Retinoid Receptor, GSK-3β, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Target Therapy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact