13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(5):1981-1996. doi:10.7150/thno.37621 This issue Cite
Research Paper
The c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer
1. Tianjin Medical University Cancer Institute and Hospital, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy, Tianjin's Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Tianjin, China.
2. State Key Laboratory for Oncogenes and Related Genes, Key Laboratory of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Ministry of Health, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Shanghai Institute of Digestive Disease, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, Jiangsu Engineering Research Center for MicroRNA Biology and Biotechnology, NJU Advanced Institute for Life Sciences (NAILS), School of Life Sciences, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China.
4. The Comprehensive Cancer Centre of Drum Tower Hospital, Medical School of Nanjing University and Clinical Cancer Institute of Nanjing University, Nanjing, China.
#These authors contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
Oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance is the major obstacle to the anticancer effects of chemotherapy in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play an important role in the chemoresistance of various tumors. Our objective is to clarify the underlying mechanism of miRNAs in chemoresistance and provide a potential strategy to improve the response of CRC patients to chemotherapeutics.
Methods: MiRNA microarray and Real-time PCR were performed to compare changes in miRNA expression between oxaliplatin-resistant and the parental cells. CCK8, apoptosis assay, immunofluorescence and xenograft studies were used to elucidate the impact of miR-27b-3p on regulating chemoresistance. Luciferase reporter assay and western blot were carried to assess the regulatory role of miR-27b-3p in ATG10 expression. The effects of miR-27b-3p and ATG10 on autophagy were investigated by GFP-LC3 fluorescence microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and western blot. ChIP assay and luciferase assay were performed to test the c-Myc's occupancy on the miR-27B promoter.
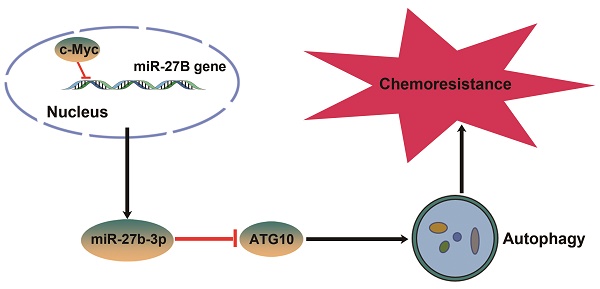
Results: We observed that miR-27b-3p expression was significantly downregulated in oxaliplatin-resistant cell lines (SW480-OxR and HCT116-OxR) compared to the corresponding parental cell lines and that miR-27b-3p expression was positively correlated with disease-free survival (DFS) time in colorectal cancer patients. MiR-27b-3p could sensitize colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin in vitro and in vivo. Under oxaliplatin treatment, chemoresistant cells showed a higher autophagy level than parental cells. Moreover, we also identified that miR-27b-3p inhibited the expression of ATG10 at the posttranscriptional level, thus inhibiting autophagy. Further study demonstrated that c-Myc can inhibit the expression of miR-27b-3p via binding to the promoter region of miR-27B gene.
Conclusions: Our study identifies a novel c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 signaling pathway that regulates colorectal cancer chemoresistance. These results suggest that miR-27b-3p is not only a potential indicator for evaluating efficiency of chemotherapy, but also a valuable therapeutic target for CRC, especially for patients with chemoresistance.
Keywords: miR-27b-3p, ATG10, chemoresistance, colorectal cancer, autophagy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact