13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(6):2587-2596. doi:10.7150/thno.40099 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Real-time colorectal cancer diagnosis using PR-OCT with deep learning
1. Department of Biomedical Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis
2. Department of Electrical & System Engineering, Washington University in St. Louis
3. Department of Surgery, Section of Colon and Rectal Surgery, Washington University School of Medicine
4. Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine
5. Department of Radiology, Washington University School of Medicine
*These authors contributed equally to this paper.
Abstract
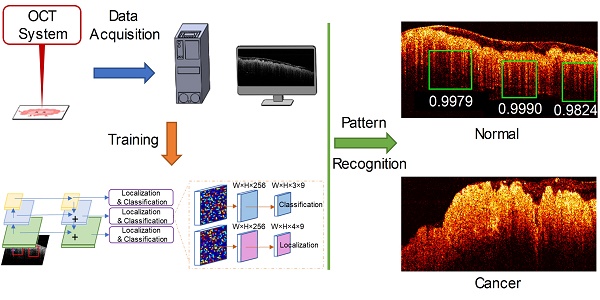
Prior reports have shown optical coherence tomography (OCT) can differentiate normal colonic mucosa from neoplasia, potentially offering an alternative technique to endoscopic biopsy - the current gold-standard colorectal cancer screening and surveillance modality. To help clinical translation limited by processing the large volume of generated data, we designed a deep learning-based pattern recognition (PR) OCT system that automates image processing and provides accurate diagnosis potentially in real-time.
Method: OCT is an emerging imaging technique to obtain 3-dimensional (3D) “optical biopsies” of biological samples with high resolution. We designed a convolutional neural network to capture the structure patterns in human colon OCT images. The network is trained and tested using around 26,000 OCT images acquired from 20 tumor areas, 16 benign areas, and 6 other abnormal areas.
Results: The trained network successfully detected patterns that identify normal and neoplastic colorectal tissue. Experimental diagnoses predicted by the PR-OCT system were compared to the known histologic findings and quantitatively evaluated. A sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 99.7% can be reached. Further, the area under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (AUC) of 0.998 is achieved.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that PR-OCT can be used to give an accurate real-time computer-aided diagnosis of colonic neoplastic mucosa. Future development of this system as an "optical biopsy" tool to assist doctors in real-time for early mucosal neoplasms screening and treatment evaluation following initial oncologic therapy is planned.
Keywords: colorectal cancer, optical coherence tomography (OCT), deep learning, optical biopsy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact