13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(7):2888-2896. doi:10.7150/thno.38882 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Auger radiopharmaceutical therapy targeting prostate-specific membrane antigen in a micrometastatic model of prostate cancer
1. Department of Radiation Oncology and Molecular Radiation Sciences, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
2. Russell H. Morgan Department of Radiology and Radiological Science, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
3. Department of Molecular and Comparative Pathobiology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
4. Current affiliation: Department of Radiation Oncology, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, NC
Abstract
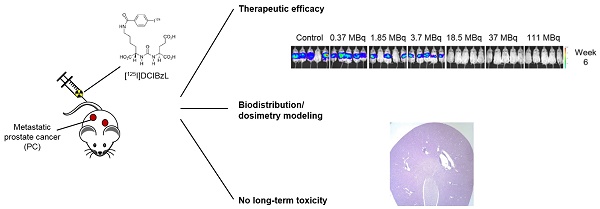
Auger radiopharmaceutical therapy is a promising strategy for micrometastatic disease given high linear energy transfer and short range in tissues, potentially limiting normal tissue toxicities. We previously demonstrated anti-tumor efficacy of a small-molecule Auger electron emitter targeting the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA), 2-[3-[1-carboxy-5-(4-[125I]iodo-benzoylamino)-pentyl]-ureido]-pentanedioic acid), or 125I-DCIBzL, in a mouse xenograft model. Here, we investigated the therapeutic efficacy, long-term toxicity, and biodistribution of 125I-DCIBzL in a micrometastatic model of prostate cancer (PC).
Methods: To test the therapeutic efficacy of 125I-DCIBzL in micrometastatic PC, we used a murine model of human metastatic PC in which PSMA+ PC3-ML cells expressing firefly luciferase were injected intravenously in NSG mice to form micrometastatic deposits. One week later, 0, 0.37, 1.85, 3.7, 18.5, 37, or 111 MBq of 125I-DCIBzL was administered (intravenously). Metastatic tumor burden was assessed using bioluminescence imaging (BLI). Long-term toxicity was evaluated via serial weights and urinalysis of non-tumor-bearing mice over a 12-month period, as well as final necropsy.
Results: In the micrometastatic PC model, activities of 18.5 MBq 125I-DCIBzL and above significantly delayed development of detectable metastatic disease by BLI and prolonged survival in mice. Gross metastases were detectable in control mice and those treated with 0.37-3.7 MBq 125I-DCIBzL at a median of 2 weeks post-treatment, versus 4 weeks for those treated with 18.5-111 MBq 125I-DCIBzL (P<0.0001 by log-rank test). Similarly, treatment with ≥18.5 MBq 125I-DCIBzL yielded a median survival of 11 weeks, compared with 6 weeks for control mice (P<0.0001). At 12 months, there was no appreciable toxicity via weight, urinalysis, or necropsy evaluation in mice treated with any activity of 125I-DCIBzL, which represents markedly less toxicity than the analogous PSMA-targeted α-particle emitter. Macro-to-microscale dosimetry modeling demonstrated lower absorbed dose in renal cell nuclei versus tumor cell nuclei due to lower levels of drug uptake and cellular internalization in combination with the short range of Auger emissions.
Conclusion: PSMA-targeted radiopharmaceutical therapy with the Auger emitter 125I-DCIBzL significantly delayed development of detectable metastatic disease and improved survival in a micrometastatic model of PC, with no long-term toxicities noted at 12 months, suggesting a favorable therapeutic ratio for treatment of micrometastatic PC.
Keywords: Auger, radiopharmaceutical therapy, radionuclide therapy, PSMA, prostate cancer, micrometastatic
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact