13.3
Impact Factor
Theranostics 2020; 10(7):3000-3021. doi:10.7150/thno.40798 This issue Cite
Research Paper
CNTNAP4 deficiency in dopaminergic neurons initiates parkinsonian phenotypes
1. Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China.
2. Key Laboratory of Neurological Function and Health, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China.
3. Information center of Guangzhou Power Supply Bureau Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510620, China.
4. The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China.
5. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510260, China.
6. School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China.
7. Shenzhen Research Institute of Xiamen University, Shenzhen 518000, China.
# Wenlong Zhang and Miaomiao Zhou contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
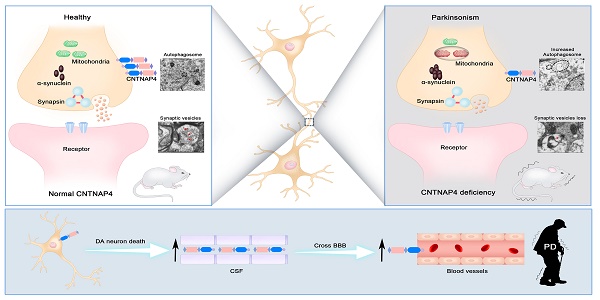
Rationale: Contactin-associated protein-like 4 (CNTNAP4) belongs to the neurexin superfamily and has critical functions in neurological development and synaptic function. Loss of CNTNAP4 in interneurons has been linked to autism, schizophrenia, and epilepsy. CNTNAP4 is also highly enriched in dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantia nigra (SN), however, few studies have investigated the role of CNTNAP4 in DA neurons, and whether CNTNAP4 deficiency in DA neurons contributes to Parkinson's disease (PD) remains unclear.
Methods: Effects of CNTNAP4 knockdown or overexpression on the DA MN9D cell line were assessed via Western blotting, immunocytochemistry, and RNA sequencing. An in vivo animal model, including CNTNAP4 knockout mice and stereotaxic injections of adeno-associated viral short-hairpin RNA with the tyrosine-hydroxylase promotor to silence CNTNAP4 in the SN, as well as the resulting physiological/behavioral effects, were evaluated via behavioral tests, Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and transmission electron microscopy. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) were performed to examine the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and plasma CNTNAP4 concentrations in PD patients.
Results: We demonstrated that CNTNAP4 knockdown induced mitophagy and increased α-synuclein expression in MN9D cells. CNTNAP4 knockdown in the SN induced PD-like increases in SN-specific α-synuclein expression, DA neuronal degeneration, and motor dysfunction in mice. In addition, CNTNAP4 knockdown in SN-DA neurons increased autophagosomes and reduced synaptic vesicles in the SN. Furthermore, CNTNAP4 knockout mice showed movement deficits, nigral DA degeneration, and increased autophagy, which were consistent with the SN-specific knockdown model. We also found that CSF and plasma CNTNAP4 expression was increased in PD patients; in particular, plasma CNTNAP4 was increased in male PD patients compared with controls or female PD patients.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that CNTNAP4 deficiency may initiate phenotypes relevant to PD, of which we elucidated some of the underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Parkinson's disease, CNTNAP4, dopaminergic neurons, α-synuclein, mitophagy
 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact